Product Description
MMC New Off Road Golf cart LithiumBattery 4 Seater Electric Golf Cart For Sale
Product Description
Product Name |
Electric Golf Cart |
Passenger capacity |
2-4-6-8-10-12 seats |
External Dimensions |
2950*1250*2000mm |
Range |
80-100km (Can be customized) |
System voltage |
48V/60V/72V |
Curb weight |
480-760kgs |
Electric Control |
Empower 3528 electric control |
The Battery |
100Ah 12V Lead-acid/ Lithium battery |
The Motor |
4-5-7KW |
Dashboard |
Electricity meter, key switch |
Body & Roof |
Fiberglass +ABS/ PP Plastic |
Windshield |
One-piece see-through POLYCARBONATE glass |
Seats |
Sponge + PU leather, white |
Bumper |
front and rear bumper |
Tire |
The golf course uses tubeless tires |
Chassis |
Steel frame with antirust and spray paint |
Color Option |
White, Red, Green, Blue, customized colors |
Modified |
Manufacture according to customer requirementsAmbulance, farmer’s car, box truck, wheelchair-capable car, solar energy, etc. |
Detailed Photos
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang CZPT Machinery Co., Ltd. Specializes in the production and sales of Electric golf carts, Sightseeing car, 3 wheeled electric vehicles, 4 wheeled electric vehicles, ATVs, UTV, electric scooter, electric bicycle, etc. A complete variety can be customized and OEM. We take talent as the foundation and technological technology Technology as the support, market-oriented, focus on creating a strong, core competition an international enterprise with strong competitiveness.
Our Advantages
★Factory-direct price
★Under min OEM order accepted
★QUICK DESIGN turnaround time
★SHORTER SAMPLE lead time
★Product tested by AUTHORIZED THIRD PARTIES
★Provide quick technical answers
★Shorter after-sales response time, within 12 hours
FAQ
Q1. If there is any technical help after we receive the carts?
A: Yes, we supply 24 hours online service for free.
Q2.Do you have CE documents and other documents forcustoms clearance?
A: Yes, we have CE, after shipment, we will send you the Packing
list/Commercial Invoice/Sales contract for customs clearance.
Q3. lf l want to visit your factory, how can l contact you?
A: Just send us your online contact number, we will discuss and make adetailed arrangement according to your time.
Q4. lf there are some problems with some parts during the warranty period, will your company repair or replace me?
A: Yes, we will send new carts parts to you within warranty time for free. Not including the consumable parts and Man-made damage.
Q5.How long can the carts be delivered?
A: Common cartss can be delivered within 3~10 working days.
| Type: | Buggy/Golf Carts |
|---|---|
| Seats: | 3-4 |
| Power: | 4000W/5000W |
| Samples: |
US$ 4515/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | Order Sample 2950*1250*2000mm(L*W*H)
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How to Design a Forging Spur Gear
Before you start designing your own spur gear, you need to understand its main components. Among them are Forging, Keyway, Spline, Set screw and other types. Understanding the differences between these types of spur gears is essential for making an informed decision. To learn more, keep reading. Also, don’t hesitate to contact me for assistance! Listed below are some helpful tips and tricks to design a spur gear. Hopefully, they will help you design the spur gear of your dreams.
Forging spur gears
Forging spur gears is one of the most important processes of automotive transmission components. The manufacturing process is complex and involves several steps, such as blank spheroidizing, hot forging, annealing, phosphating, and saponification. The material used for spur gears is typically 20CrMnTi. The process is completed by applying a continuous through extrusion forming method with dies designed for the sizing band length L and Splitting angle thickness T.
The process of forging spur gears can also use polyacetal (POM), a strong plastic commonly used for the manufacture of gears. This material is easy to mold and shape, and after hardening, it is extremely stiff and abrasion resistant. A number of metals and alloys are used for spur gears, including forged steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. Listed below are the different types of materials used in gear manufacturing and their advantages and disadvantages.
A spur gear’s tooth size is measured in modules, or m. Each number represents the number of teeth in the gear. As the number of teeth increases, so does its size. In general, the higher the number of teeth, the larger the module is. A high module gear has a large pressure angle. It’s also important to remember that spur gears must have the same module as the gears they are used to drive.
Set screw spur gears
A modern industry cannot function without set screw spur gears. These gears are highly efficient and are widely used in a variety of applications. Their design involves the calculation of speed and torque, which are both critical factors. The MEP model, for instance, considers the changing rigidity of a tooth pair along its path. The results are used to determine the type of spur gear required. Listed below are some tips for choosing a spur gear:
Type A. This type of gear does not have a hub. The gear itself is flat with a small hole in the middle. Set screw gears are most commonly used for lightweight applications without loads. The metal thickness can range from 0.25 mm to 3 mm. Set screw gears are also used for large machines that need to be strong and durable. This article provides an introduction to the different types of spur gears and how they differ from one another.
Pin Hub. Pin hub spur gears use a set screw to secure the pin. These gears are often connected to a shaft by dowel, spring, or roll pins. The pin is drilled to the precise diameter to fit inside the gear, so that it does not come loose. Pin hub spur gears have high tolerances, as the hole is not large enough to completely grip the shaft. This type of gear is generally the most expensive of the three.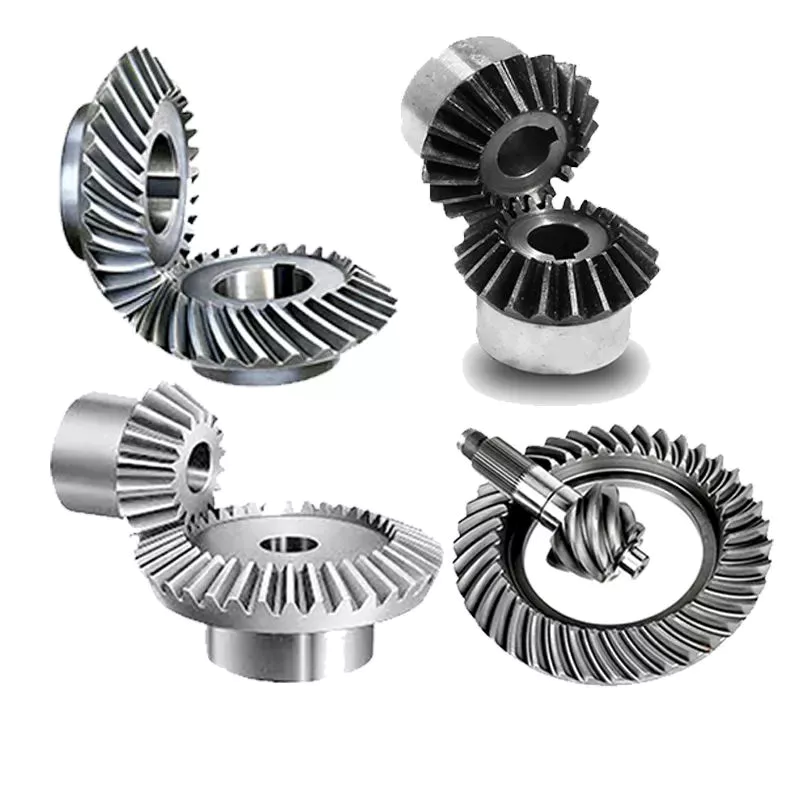
Keyway spur gears
In today’s modern industry, spur gear transmissions are widely used to transfer power. These types of transmissions provide excellent efficiency but can be susceptible to power losses. These losses must be estimated during the design process. A key component of this analysis is the calculation of the contact area (2b) of the gear pair. However, this value is not necessarily applicable to every spur gear. Here are some examples of how to calculate this area. (See Figure 2)
Spur gears are characterized by having teeth parallel to the shafts and axis, and a pitch line velocity of up to 25 m/s is considered high. In addition, they are more efficient than helical gears of the same size. Unlike helical gears, spur gears are generally considered positive gears. They are often used for applications in which noise control is not an issue. The symmetry of the spur gear makes them especially suitable for applications where a constant speed is required.
Besides using a helical spur gear for the transmission, the gear can also have a standard tooth shape. Unlike helical gears, spur gears with an involute tooth form have thick roots, which prevents wear from the teeth. These gears are easily made with conventional production tools. The involute shape is an ideal choice for small-scale production and is one of the most popular types of spur gears.
Spline spur gears
When considering the types of spur gears that are used, it’s important to note the differences between the two. A spur gear, also called an involute gear, generates torque and regulates speed. It’s most common in car engines, but is also used in everyday appliances. However, one of the most significant drawbacks of spur gears is their noise. Because spur gears mesh only one tooth at a time, they create a high amount of stress and noise, making them unsuitable for everyday use.
The contact stress distribution chart represents the flank area of each gear tooth and the distance in both the axial and profile direction. A high contact area is located toward the center of the gear, which is caused by the micro-geometry of the gear. A positive l value indicates that there is no misalignment of the spline teeth on the interface with the helix hand. The opposite is true for negative l values.
Using an upper bound technique, Abdul and Dean studied the forging of spur gear forms. They assumed that the tooth profile would be a straight line. They also examined the non-dimensional forging pressure of a spline. Spline spur gears are commonly used in motors, gearboxes, and drills. The strength of spur gears and splines is primarily dependent on their radii and tooth diameter.
SUS303 and SUS304 stainless steel spur gears
Stainless steel spur gears are manufactured using different techniques, which depend on the material and the application. The most common process used in manufacturing them is cutting. Other processes involve rolling, casting, and forging. In addition, plastic spur gears are produced by injection molding, depending on the quantity of production required. SUS303 and SUS304 stainless steel spur gears can be made using a variety of materials, including structural carbon steel S45C, gray cast iron FC200, nonferrous metal C3604, engineering plastic MC901, and stainless steel.
The differences between 304 and 303 stainless steel spur gears lie in their composition. The two types of stainless steel share a common design, but have varying chemical compositions. China and Japan use the letters SUS304 and SUS303, which refer to their varying degrees of composition. As with most types of stainless steel, the two different grades are made to be used in industrial applications, such as planetary gears and spur gears.
Stainless steel spur gears
There are several things to look for in a stainless steel spur gear, including the diametral pitch, the number of teeth per unit diameter, and the angular velocity of the teeth. All of these aspects are critical to the performance of a spur gear, and the proper dimensional measurements are essential to the design and functionality of a spur gear. Those in the industry should be familiar with the terms used to describe spur gear parts, both to ensure clarity in production and in purchase orders.
A spur gear is a type of precision cylindrical gear with parallel teeth arranged in a rim. It is used in various applications, such as outboard motors, winches, construction equipment, lawn and garden equipment, turbine drives, pumps, centrifuges, and a variety of other machines. A spur gear is typically made from stainless steel and has a high level of durability. It is the most commonly used type of gear.
Stainless steel spur gears can come in many different shapes and sizes. Stainless steel spur gears are generally made of SUS304 or SUS303 stainless steel, which are used for their higher machinability. These gears are then heat-treated with nitriding or tooth surface induction. Unlike conventional gears, which need tooth grinding after heat-treating, stainless steel spur gears have a low wear rate and high machinability.


editor by CX 2023-11-11
China 2023 New Design ! Good Quality CZPT 4-6 Bit CNC Router Machine Vacuum Table 4 Zone for Wood and Melamine browning gear rack
Condition: New
Range of Spindle Speed(r.p.m): 1 – 24000 rpm
Positioning Accuracy (mm): 0.05 mm
Number of Axes: 3
No. of Spindles: Single
Working Table Size(mm): 1300×2500
Machine Type: CNC Router
Travel (X Axis)(mm): 1300 mm
Travel (Y Axis)(mm): 2500 mm
Repeatability (X/Y/Z) (mm): 0.05 mm
Spindle Motor Power(kW): 9
CNC or Not: CNC
Voltage: 220v/380v
Dimension(L*W*H): 3650*2200*1800mm
Power (kW): 9
Weight (KG): 1500
Control System Brand: Mach3
Warranty: 2 years
Key Selling Points: High-accuracy
Applicable Industries: Hotels, Garment Shops, Building Material Shops, Machinery Repair Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms, River Land Amphibious Driving vehicle ATV Car for Sale China Manufacture Restaurant, Home Use, Retail, Food Shop, Printing Shops, Construction works , Energy & Mining, 2VP245 14HP TX CZPT Dual Stage air conditioning vacuum pump refrigeration 220v50hz Food & Beverage Shops, Advertising Company
Machinery Test Report: Provided
Video outgoing-inspection: Provided
Warranty of core components: 2 years
Core Components: Bearing, Motor, Pump
Product name: CZPT CNC Router Machine
Working table: Vacuum Table + T-Slot
Control system: NcStudio Control System
Working area: 1300*2500mm
Spindle: 9kw Air Cooling Spindle
Weight: 1500kg
Xihu (West Lake) Dis. rail: ZheJiang CZPT Square Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Rail
Transmission: XY Axis Gear Rack
Driving system: Japan CZPT Servo System
Working voltage: AC380V/3PH/50Hz(option:220V)
Packaging Details: plywood box, free from fumigation for YK-960 cnc co2 laser cutting machines.
Port: HangZhou
Features
1. With 8 or 12 sets of tools to change automatically, which can saving time of tools changing and improving working efficiency.
2.Vacuum table using high-density material with great suction strength, comfortably accommadating all sizes of work piece.
3.control system is simple, Special Worm Reducer For Tyre Changer Speed Gear Box worm shaft gearbox convenient and easy to learn, users can quickly get the fleciblity to master the use of equipment, strong independence.
4.The frame adopts the gantry column structure, the machine parts are produced and assembled with extremely high precision to ensure the high performance and stability of the machine, excellent quality and tolerance.
| Model | 1325 CZPT cnc router |
| Spindle | 9kw CZPT air cooling spindle |
| Tool magazine | In-line tool magazine (8-12 Tools) |
| Working table | Vacuum & T-slot table |
| Transmission mode | Z axis ZheJiang TBI screw |
| Drive | Yaskawa/Leadshine Servo Motor with Drive |
| Inverter | Xihu (West Lake) Dis./Delta Brand |
| Control system | Syntec/Weihong |
| Filter | Prevent electromagnetic interference |
| Working area | 1300*2500*300mm |
| Max working speed | 25m/min |
| Max velocity | 50m/min |
| Spindle speed | 0-24000rmp |
| Working voltage | AC220/380V |
| Interface | USB |
| Command language | G code |
| Software environment | Type3/Artcut/Artcam/Ucancam |
| Running environment | Temperature:0-45°C |
Cutting Sample
Packaging & 4×4 tractors price for agriculture farm machinery tractor cheap agricultural tractors cultivators low price for sale Shipping
Company Information
Buyer Feedback

Types of Bevel Gears
Bevel Gears are used in a number of industries. They are used in wheeled excavators, dredges, conveyor belts, mill actuators, and rail transmissions. A bevel gear’s spiral or angled bevel can make it suitable for confined spaces. It is also used in robotics and vertical supports of rolling mills. You can use bevel gears in food processing processes. For more information on bevel gears, read on.
Spiral bevel gear
Spiral bevel gears are used to transmit power between two shafts in a 90-degree orientation. They have curved or oblique teeth and can be fabricated from various metals. Bestagear is one manufacturer specializing in medium to large spiral bevel gears. They are used in the mining, metallurgical, marine, and oil fields. Spiral bevel gears are usually made from steel, aluminum, or phenolic materials.
Spiral bevel gears have many advantages. Their mesh teeth create a less abrupt force transfer. They are incredibly durable and are designed to last a long time. They are also less expensive than other right-angle gears. They also tend to last longer, because they are manufactured in pairs. The spiral bevel gear also reduces noise and vibration from its counterparts. Therefore, if you are in need of a new gear set, spiral bevel gears are the right choice.
The contact between spiral bevel gear teeth occurs along the surface of the gear tooth. The contact follows the Hertz theory of elastic contact. This principle holds for small significant dimensions of the contact area and small relative radii of curvature of the surfaces. In this case, strains and friction are negligible. A spiral bevel gear is a common example of an inverted helical gear. This gear is commonly used in mining equipment.
Spiral bevel gears also have a backlash-absorbing feature. This feature helps secure the thickness of the oil film on the gear surface. The shaft axis, mounting distance, and angle errors all affect the tooth contact on a spiral bevel gear. Adjusting backlash helps to correct these problems. The tolerances shown above are common for bevel gears. In some cases, manufacturers make slight design changes late in the production process, which minimizes the risk to OEMs.
Straight bevel gear
Straight bevel gears are among the easiest types of gears to manufacture. The earliest method used to manufacture straight bevel gears was to use a planer equipped with an indexing head. However, improvements have been made in manufacturing methods after the introduction of the Revacycle system and the Coniflex. The latest technology allows for even more precise manufacturing. Both of these manufacturing methods are used by CZPT. Here are some examples of straight bevel gear manufacturing.
A straight bevel gear is manufactured using two kinds of bevel surfaces, namely, the Gleason method and the Klingelnberg method. Among the two, the Gleason method is the most common. Unlike other types of gear, the CZPT method is not a universal standard. The Gleason system has higher quality gears, since its adoption of tooth crowning is the most effective way to make gears that tolerate even small assembly errors. It also eliminates the stress concentration in the bevelled edges of the teeth.
The gear’s composition depends on the application. When durability is required, a gear is made of cast iron. The pinion is usually three times harder than the gear, which helps balance wear. Other materials, such as carbon steel, are cheaper, but are less resistant to corrosion. Inertia is another critical factor to consider, since heavier gears are more difficult to reverse and stop. Precision requirements may include the gear pitch and diameter, as well as the pressure angle.
Involute geometry of a straight bevel gear is often computed by varying the surface’s normal to the surface. Involute geometry is computed by incorporating the surface coordinates and the theoretical tooth thickness. Using the CMM, the spherical involute surface can be used to determine tooth contact patterns. This method is useful when a roll tester tooling is unavailable, because it can predict the teeth’ contact pattern.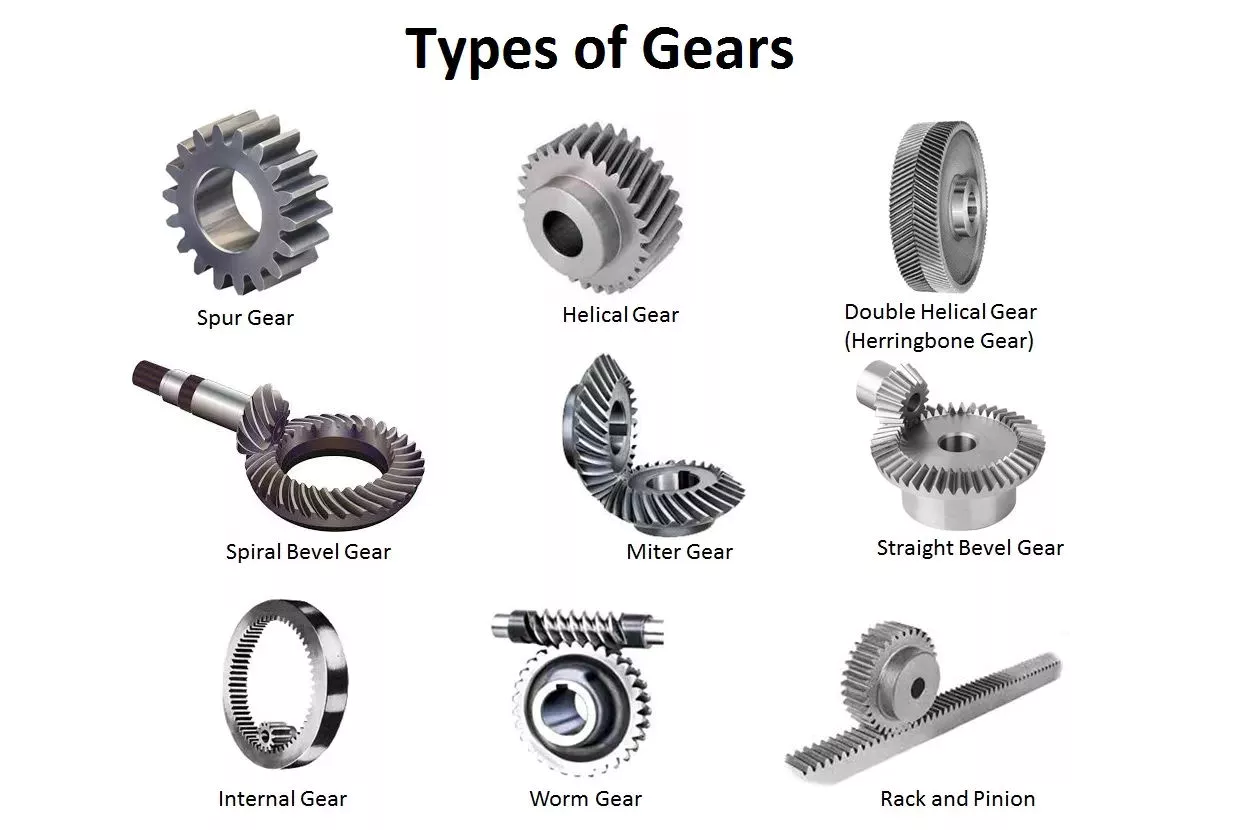
Hypoid bevel gear
Hypoid bevel gears are an efficient and versatile speed reduction solution. Their compact size, high efficiency, low noise and heat generation, and long life make them a popular choice in the power transmission and motion control industries. The following are some of the benefits of hypoid gearing and why you should use it. Listed below are some of the key misperceptions and false assumptions of this gear type. These assumptions may seem counterintuitive at first, but will help you understand what this gear is all about.
The basic concept of hypoid gears is that they use two non-intersecting shafts. The smaller gear shaft is offset from the larger gear shaft, allowing them to mesh without interference and support each other securely. The resulting torque transfer is improved when compared to conventional gear sets. A hypoid bevel gear is used to drive the rear axle of an automobile. It increases the flexibility of machine design and allows the axes to be freely adjusted.
In the first case, the mesh of the two bodies is obtained by fitting the hyperboloidal cutter to the desired gear. Its geometric properties, orientation, and position determine the desired gear. The latter is used if the desired gear is noise-free or is required to reduce vibrations. A hyperboloidal cutter, on the other hand, meshes with two toothed bodies. It is the most efficient option for modeling hypoid gears with noise concerns.
The main difference between hypoid and spiral bevel gears is that the hypoid bevel gear has a larger diameter than its counterparts. They are usually found in 1:1 and 2:1 applications, but some manufacturers also provide higher ratios. A hypoid gearbox can achieve speeds of three thousand rpm. This makes it the preferred choice in a variety of applications. So, if you’re looking for a gearbox with a high efficiency, this is the gear for you.
Addendum and dedendum angles
The addendum and dedendum angles of a bevel gear are used to describe the shape and depth of the teeth of the gear. Each tooth of the gear has a slightly tapered surface that changes in depth. These angles are defined by their addendum and dedendum distances. Addendum angle is the distance between the top land and the bottom surface of the teeth, while dedendum angle is the distance between the pitch surface and the bottom surface of the teeth.
The pitch angle is the angle formed by the apex point of the gear’s pitch cone with the pitch line of the gear shaft. The dedendum angle, on the other hand, is the depth of the tooth space below the pitch line. Both angles are used to measure the shape of a bevel gear. The addendum and dedendum angles are important for gear design.
The dedendum and addendum angles of a bevel gear are determined by the base contact ratio (Mc) of the two gears. The involute curve is not allowed to extend within the base diameter of the bevel gear. The base diameter is also a critical measurement for the design of a gear. It is possible to reduce the involute curve to match the involute curve, but it must be tangential to the involute curve.
The most common application of a bevel gear is the automotive differential. They are used in many types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, and even construction equipment. They are also used in the marine industry and aviation. Aside from these two common uses, there are many other uses for bevel gears. And they are still growing in popularity. But they’re a valuable part of automotive and industrial gearing systems.
Applications of bevel gears
Bevel gears are used in a variety of applications. They are made of various materials depending on their weight, load, and application. For high-load applications, ferrous metals such as grey cast iron are used. These materials have excellent wear resistance and are inexpensive. For lower-weight applications, steel or non-metals such as plastics are used. Some bevel gear materials are considered noiseless. Here are some of their most common uses.
Straight bevel gears are the easiest to manufacture. The earliest method of manufacturing them was with a planer with an indexing head. Modern manufacturing methods introduced the Revacycle and Coniflex systems. For industrial gear manufacturing, the CZPT uses the Revacycle system. However, there are many types of bevel gears. This guide will help you choose the right material for your next project. These materials can withstand high rotational speeds and are very strong.
Bevel gears are most common in automotive and industrial machinery. They connect the driveshaft to the wheels. Some even have a 45-degree bevel. These gears can be placed on a bevel surface and be tested for their transmission capabilities. They are also used in testing applications to ensure proper motion transmission. They can reduce the speed of straight shafts. Bevel gears can be used in many industries, from marine to aviation.
The simplest type of bevel gear is the miter gear, which has a 1:1 ratio. It is used to change the axis of rotation. The shafts of angular miter bevel gears can intersect at any angle, from 45 degrees to 120 degrees. The teeth on the bevel gear can be straight, spiral, or Zerol. And as with the rack and pinion gears, there are different types of bevel gears.


editor by Cx2023-07-13
China 2022 Hot Selling 1325 1530 Wood Router 4 Axis 3 Axis CNC Wood Carving Engraving Machine CNC Router Woodworking Machinery Price aluminum gear rack
Condition: New
Machine Type: CNC
Video outgoing-inspection: Provided
Machinery Test Report: Provided
Marketing Type: New Product
Warranty of core components: 1 Year
Core Components: Pump
Warranty: 3 years, 3 years
Weight (KG): 1500 KG
Power (kW): 3KW
Key Selling Points: Easy to Operate
Showroom Location: Brazil, Pakistan, India
Applicable Industries: Hotels, Garment Shops, Building Material Shops, Machinery Repair Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms, Restaurant, Home Use, Retail, Food Shop, Printing Shops, Construction works , Energy & Mining, Food & Beverage Shops, Other, Advertising Company
Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Rail: Square Rail with X,Y,Z axis
X Y Z Transmission: Gear rack with X and Y axis Imported Ball Screw with Z axis
Spindle Motor: 3KW 5.5KW etc
Inverter: 3.7KW inverter
Control System: NC DSP for reference
Typeset Software: Type3(English)/Ucancam
Motor: stepper and servo motor can be choosen
Worktable: T slot and vacuum worktable
Name: Cnc Wood Router
Packaging Details: International standard package for CZPT CO2 Laser Engraving Cutting Machine.
Port: ZheJiang , HangZhou, ZheJiang
2571 Hot Selling 1325 1530 Wood Router 4 Axis 3 Axis CNC Wood Carving Engraving Machine CNC Router Woodworking Machinery PriceFurniture making 1325 Wood mdf cnc router machine is also called 3 axis CNC Wood Router machine. With popular working size of 1325(1300×2500mm), we have 1530, 2030 can be made. Or other size, it can be customized. it is suitable for wooden industry, furniture industry, technology research, advertising design, arts creation, and hobby purposes. Product details 3kw water cooling spindleHigher efficiency and more time savingWe have water cooling spindles and Air cooling spindles for your choosing.engraves more smoothly and uses for long time. Fully programmable speeds from 6000 to 24000 RPM, more powerful and less noise. DSP A11 control system1.Support drive and spindle error alarm function2.Large storage space, perfect U disk compatibility,fast reading speed, Factory Custom High Quality Braa steel CNC Turning Parts Throttle Shaft of Carburetor safe and reliable U disk-processing.3.Support intelligent file checking function.4.Parameter backup and restore function to prevent theloss of important parameters.5.High anti-jamming intensity passes many CE tests. Vacuum pumpThis vacuum pump using with Vacuum worktable together. This series of vacuum adsorption pumps is energy-saving and energy-saving, low noise, corrosion resistance, strong adsorption force, economical and practical, and solves the problem of plate offset in the engraving process of woodworking equipment and improves the accuracy of machine tool plate engraving. ToolsSemi-Automatic PET Bottle Blowing Machine Bottle Making Machine Bottle Moulding MachinePET Bottle Making Machine is suitable for producing PET plastic containers and bottles in all shapes. Dual bag dust collectorThe bag vacuum cleaner has a strong suction power. Mobile bag vacuum cleaner use: can be close to the dust place to collect dust, no piping is needed, saving money, greatly improving convenience and mobility Specification
| Machine Model | TS1325 CNC ROUTER |
| Working area | 1300x2500mm or 1500x3000mm (Size can be customized) |
| Working Voltage | 380V/3PH/50Hz (option) |
| Spindle | 3kw water Spindles |
| Spindle Speed | 0-24000RPM or 18000rpm |
| Inverter | 5.5 KW Xihu (West Lake) Dis. inverter |
| Drive Motors | Leadshine 860H |
| Frame | New Type Heavy Duty Body |
| Lubrication | Manual Lubrication System |
| Gantry structure | Steel Gantry |
| Option | Automatic Oil Mist Cooling |

Types of Miter Gears
The different types of miter gears include Hypoid, Crown, and Spiral. To learn more, read on. In addition, you’ll learn about their differences and similarities. This article will provide an overview of the different types of miter gears. You can also choose the type that fits your needs by using the guide below. After you’ve read it, you’ll know how to use them in your project. You’ll also learn how to pair them up by hand, which is particularly useful if you’re working on a mechanical component.
Bevel gears
Bevel and miter gears are both used to connect two shafts that have different axes. In most cases, these gears are used at right angles. The pitch cone of a bevel gear has the same shape as that of a spur gear, except the tooth profile is slightly tapered and has variable depth. The pinions of a bevel gear are normally straight, but can be curved or skew-shaped. They can also have an offset crown wheel with straight teeth relative to the axis.
In addition to their industrial applications, miter gears are found in agriculture, bottling, printing, and various industrial sectors. They are used in coal mining, oil exploration, and chemical processes. They are an important part of conveyors, elevators, kilns, and more. In fact, miter gears are often used in machine tools, like forklifts and jigsaws.
When considering which gear is right for a certain application, you’ll need to think about the application and the design goals. For example, you’ll want to know the maximum load that the gear can carry. You can use computer simulation programs to determine the exact torque required for a specific application. Miter gears are bevel gears that are geared on a single axis, not two.
To calculate the torque required for a particular application, you’ll need to know the MA of each bevel gear. Fortunately, you can now do so with CZPT. With the help of this software, you can generate 3D models of spiral bevel gears. Once you’ve created your model, you can then machine it. This can make your job much easier! And it’s fun!
In terms of manufacturing, straight bevel gears are the easiest to produce. The earliest method for this type of gear is a planer with an indexing head. Since the development of CNC machining, however, more effective manufacturing methods have been developed. These include CZPT, Revacycle, and Coniflex systems. The CZPT uses the Revacycle system. You can also use a CNC mill to manufacture spiral bevel gears.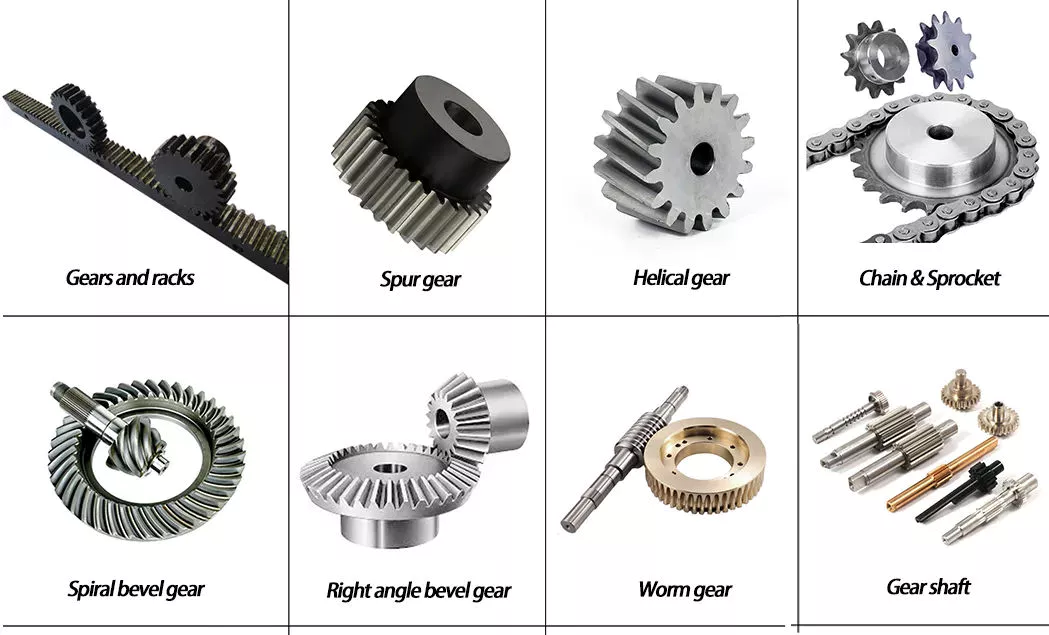
Hypoid bevel gears
When it comes to designing hypoid bevel gears for miter and other kinds of gears, there are several important parameters to consider. In order to produce high-quality gearings, the mounting distance between the gear teeth and the pinion must be within a predefined tolerance range. In other words, the mounting distance between the gear teeth and pinion must be 0.05 mm or less.
To make this possible, the hypoid bevel gearset mesh is designed to involve sliding action. The result is a quiet transmission. It also means that higher speeds are possible without increasing noise levels. In comparison, bevel gears tend to be noisy at high speeds. For these reasons, the hypoid gearset is the most efficient way to build miter gears. However, it’s important to keep in mind that hypoid gears are not for every application.
Hypoid bevel gears are analogous to spiral bevels, but they don’t have intersecting axes. Because of this, they can produce larger pinions with smooth engagement. Crown bevel gears, on the other hand, have a 90-degree pitch and parallel teeth. Their geometry and pitch is unique, and they have particular geometrical properties. There are different ways to express pitch. The diametral pitch is the number of teeth, while circumferential measurement is called the circumference.
The face-milling method is another technique used for the manufacture of hypoid and spiral bevel gears. Face-milling allows gears to be ground for high accuracy and surface finish. It also allows for the elimination of heat treatment and facilitates the creation of predesigned ease-off topographies. Face-milling increases mechanical resistance by as much as 20%. It also reduces noise levels.
The ANSI/AGMA/ISO standards for geometric dimensioning differ from the best practices for manufacturing hypoid and bevel gears. The violation of common datum surfaces leads to a number of geometrical dimensioning issues. Moreover, hypoid gears need to be designed to incorporate the base pitches of the mating pinion and the hypoid bevel gear. This is not possible without knowing the base pitch of the gear and the mating pinion.
Crown bevel gears
When choosing crown bevels for a miter gear, you will need to consider a number of factors. Specifically, you will need to know the ratio of the tooth load to the bevel gear pitch radius. This will help you choose a bevel gear that possesses the right amount of excitation and load capacity. Crown bevels are also known as helical gears, which are a combination of two bevel gear types.
These bevel gears differ from spiral bevels because the bevels are not intersected. This gives you the flexibility of using a larger pinion and smoother engagement. Crown bevel gears are also named for their different tooth portions: the toe, or the part of the gear closest to the bore, and the heel, or the outermost diameter. The tooth height is smaller at the toe than it is at the heel, but the height of the gear is the same at both places.
Crown bevel gears are cylindrical, with teeth that are angled at an angle. They have a 1:1 gear ratio and are used for miter gears and spur gears. Crown bevel gears have a tooth profile that is the same as spur gears but is slightly narrower at the tip, giving them superior quietness. Crown bevel gears for miter gears can be made with an offset pinion.
There are many other options available when choosing a Crown bevel gear for miter gears. The material used for the gears can vary from plastics to pre-hardened alloys. If you are concerned with the material’s strength, you can choose a pre-hardened alloy with a 32-35 Rc hardness. This alloy also has the advantage of being more durable than plastic. In addition to being stronger, crown bevel gears are also easier to lubricate.
Crown bevel gears for miter gears are similar to spiral bevels. However, they have a hyperbolic, not conical, pitch surface. The pinion is often offset above or below the center of the gear, which allows for a larger diameter. Crown bevel gears for miter gears are typically larger than hypoid gears. The hypoid gear is commonly used in automobile rear axles. They are useful when the angle of rotation is 90 degrees. And they can be used for 1:1 ratios.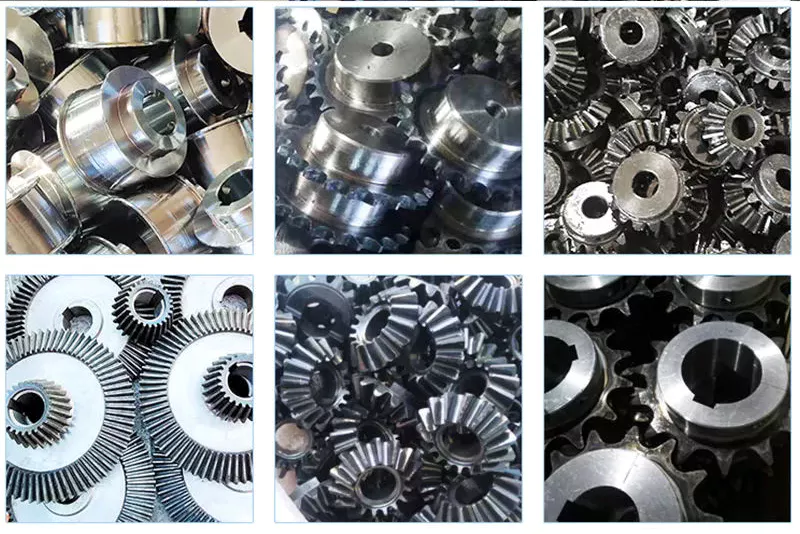
Spiral miter gears
Spiral bevel gears are produced by machining the face surface of the teeth. The process follows the Hertz theory of elastic contact, where the dislocations are equivalent to small significant dimensions of the contact area and the relative radii of curvature. This method assumes that the surfaces are parallel and that the strains are small. Moreover, it can reduce noise. This makes spiral bevel gears an ideal choice for high-speed applications.
The precision machining of CZPT spiral miter gears reduces backlash. They feature adjustable locking nuts that can precisely adjust the spacing between the gear teeth. The result is reduced backlash and maximum drive life. In addition, these gears are flexible enough to accommodate design changes late in the production process, reducing risk for OEMs and increasing efficiency and productivity. The advantages of spiral miter gears are outlined below.
Spiral bevel gears also have many advantages. The most obvious of these advantages is that they have large-diameter shafts. The larger shaft size allows for a larger diameter gear, but this means a larger gear housing. In turn, this reduces ground clearance, interior space, and weight. It also makes the drive axle gear larger, which reduces ground clearance and interior space. Spiral bevel gears are more efficient than spiral bevel gears, but it may be harder to find the right size for your application.
Another benefit of spiral miter gears is their small size. For the same amount of power, a spiral miter gear is smaller than a straight cut miter gear. Moreover, spiral bevel gears are less likely to bend or pit. They also have higher precision properties. They are suitable for secondary operations. Spiral miter gears are more durable than straight cut ones and can operate at higher speeds.
A key feature of spiral miter gears is their ability to resist wear and tear. Because they are constantly being deformed, they tend to crack in a way that increases their wear and tear. The result is a harder gear with a more contoured grain flow. But it is possible to restore the quality of your gear through proper maintenance. If you have a machine, it would be in your best interest to replace worn parts if they aren’t functioning as they should.


editor by Cx2023-07-13
China 2 Lugs 4 Lugs 6 Lugs Nylon Gear Rack With Screws For Sliding Gate Opener steering gear rack
Condition: New
Warranty: 6 Months
Shape: Rack Gear
Applicable Industries: Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Farms, Home Use, Construction works , Other, Advertising Company
Weight (KG): 4
Showroom Location: Canada, United Kingdom, Italy, France, Philippines, Peru, Morocco, Kenya, UAE, Colombia, Kazakhstan, Nigeria, Uzbekistan, Best selling Star Product Super High Efficiency Original Agriculture RiceCornWheat Combine Harvester Hot Sale Malaysia
Video outgoing-inspection: Provided
Machinery Test Report: Provided
Marketing Type: New Product 2571
Warranty of core components: 6 Months
Core Components: Gear
Model Number: Gear
Material: Stainless steel, Steel, Q235steel/Nylon
Processing: Precision Casting
Standard or Nonstandard: Nonstandard
Product Name: Steel Material and Rack Gear Shape Gear Rack Pinion
Keyword: Gear Rack
Tooth Profile: Straight or Helical
Module:: M1-M8
Surface Treatment: Carbonization, Case Hardenning
Size: Customized Accepted
Application: Hotels, Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant,
Process: Heat Treatment+CNC Machining
Service: ODM OEM Srvice
Packaging Details: Carton
Port: ZheJiang
Products Description OEM&ODM(Rack Gear).We can make standard/special Gear andGear Rack according to drawings or samples. Gear material can be carbon steel, stainlesssteel, aluminium, copper, brass etc. Tell us your requirements today. Get a Free Quotation via Us >>> GoHigh Precision Cnc Straight Helical Gear Rack And Pinions Factory Characteristics of Rack And Pinion★The tooth surface of the fine-milling rack is processed by fine-milling, and the multiple finishing processes ensure that thetooth surface has small deformation and high consistency. ★The precision of the precision milling rack can reach grade 5, and the precision is high. ★The whole rack is quenched and tempered, all surfaces except the tooth surface are ironed, and the positioningaccuracy is high. ★Affordable price, widely used in automation, Widely Used Superior Quality Magnetic Couplings Industrial Magnetic Drive Shaft Coupling robotics, automatic welding and other fields. Specification
| Code | |||||
| Both Ends Processing | Economical | Material | Surface Treatment | ||
| KLDAA | KLDBB | S45C | Iron tetroxide protective film | ||
| KLDCC | S45C | High-frequency quenching, blackened surface | |||

The Difference Between Planetary Gears and Spur Gears
A spur gear is a type of mechanical drive that turns an external shaft. The angular velocity is proportional to the rpm and can be easily calculated from the gear ratio. However, to properly calculate angular velocity, it is necessary to know the number of teeth. Fortunately, there are several different types of spur gears. Here’s an overview of their main features. This article also discusses planetary gears, which are smaller, more robust, and more power-dense.
Planetary gears are a type of spur gear
One of the most significant differences between planetary gears and spurgears is the way that the two share the load. Planetary gears are much more efficient than spurgears, enabling high torque transfer in a small space. This is because planetary gears have multiple teeth instead of just one. They are also suitable for intermittent and constant operation. This article will cover some of the main benefits of planetary gears and their differences from spurgears.
While spur gears are more simple than planetary gears, they do have some key differences. In addition to being more basic, they do not require any special cuts or angles. Moreover, the tooth shape of spur gears is much more complex than those of planetary gears. The design determines where the teeth make contact and how much power is available. However, a planetary gear system will be more efficient if the teeth are lubricated internally.
In a planetary gear, there are three shafts: a sun gear, a planet carrier, and an external ring gear. A planetary gear is designed to allow the motion of one shaft to be arrested, while the other two work simultaneously. In addition to two-shaft operation, planetary gears can also be used in three-shaft operations, which are called temporary three-shaft operations. Temporary three-shaft operations are possible through frictional coupling.
Among the many benefits of planetary gears is their adaptability. As the load is shared between several planet gears, it is easier to switch gear ratios, so you do not need to purchase a new gearbox for every new application. Another major benefit of planetary gears is that they are highly resistant to high shock loads and demanding conditions. This means that they are used in many industries.
They are more robust
An epicyclic gear train is a type of transmission that uses concentric axes for input and output. This type of transmission is often used in vehicles with automatic transmissions, such as a Lamborghini Gallardo. It is also used in hybrid cars. These types of transmissions are also more robust than conventional planetary gears. However, they require more assembly time than a conventional parallel shaft gear.
An epicyclic gearing system has three basic components: an input, an output, and a carrier. The number of teeth in each gear determines the ratio of input rotation to output rotation. In some cases, an epicyclic gear system can be made with two planets. A third planet, known as the carrier, meshes with the second planet and the sun gear to provide reversibility. A ring gear is made of several components, and a planetary gear may contain many gears.
An epicyclic gear train can be built so that the planet gear rolls inside the pitch circle of an outer fixed gear ring, or “annular gear.” In such a case, the curve of the planet’s pitch circle is called a hypocycloid. When epicycle gear trains are used in combination with a sun gear, the planetary gear train is made up of both types. The sun gear is usually fixed, while the ring gear is driven.
Planetary gearing, also known as epicyclic gear, is more durable than other types of transmissions. Because planets are evenly distributed around the sun, they have an even distribution of gears. Because they are more robust, they can handle higher torques, reductions, and overhung loads. They are also more energy-dense and robust. In addition, planetary gearing is often able to be converted to various ratios.
They are more power dense
The planet gear and ring gear of a compound planetary transmission are epicyclic stages. One part of the planet gear meshes with the sun gear, while the other part of the gear drives the ring gear. Coast tooth flanks are used only when the gear drive works in reversed load direction. Asymmetry factor optimization equalizes the contact stress safety factors of a planetary gear. The permissible contact stress, sHPd, and the maximum operating contact stress (sHPc) are equalized by asymmetry factor optimization.
In addition, epicyclic gears are generally smaller and require fewer space than helical ones. They are commonly used as differential gears in speed frames and in looms, where they act as a Roper positive let off. They differ in the amount of overdrive and undergearing ratio they possess. The overdrive ratio varies from fifteen percent to forty percent. In contrast, the undergearing ratio ranges from 0.87:1 to 69%.
The TV7-117S turboprop engine gearbox is the first known application of epicyclic gears with asymmetric teeth. This gearbox was developed by the CZPT Corporation for the Ilyushin Il-114 turboprop plane. The TV7-117S’s gearbox arrangement consists of a first planetary-differential stage with three planet gears and a second solar-type coaxial stage with five planet gears. This arrangement gives epicyclic gears the highest power density.
Planetary gearing is more robust and power-dense than other types of gearing. They can withstand higher torques, reductions, and overhung loads. Their unique self-aligning properties also make them highly versatile in rugged applications. It is also more compact and lightweight. In addition to this, epicyclic gears are easier to manufacture than planetary gears. And as a bonus, they are much less expensive.
They are smaller
Epicyclic gears are small mechanical devices that have a central “sun” gear and one or more outer intermediate gears. These gears are held in a carrier or ring gear and have multiple mesh considerations. The system can be sized and speeded by dividing the required ratio by the number of teeth per gear. This process is known as gearing and is used in many types of gearing systems.
Planetary gears are also known as epicyclic gearing. They have input and output shafts that are coaxially arranged. Each planet contains a gear wheel that meshes with the sun gear. These gears are small and easy to manufacture. Another advantage of epicyclic gears is their robust design. They are easily converted into different ratios. They are also highly efficient. In addition, planetary gear trains can be designed to operate in multiple directions.
Another advantage of epicyclic gearing is their reduced size. They are often used for small-scale applications. The lower cost is associated with the reduced manufacturing time. Epicyclic gears should not be made on N/C milling machines. The epicyclic carrier should be cast and tooled on a single-purpose machine, which has several cutters cutting through material. The epicyclic carrier is smaller than the epicyclic gear.
Epicyclic gearing systems consist of three basic components: an input, an output, and a stationary component. The number of teeth in each gear determines the ratio of input rotation to output rotation. Typically, these gear sets are made of three separate pieces: the input gear, the output gear, and the stationary component. Depending on the size of the input and output gear, the ratio between the two components is greater than half.
They have higher gear ratios
The differences between epicyclic gears and regular, non-epicyclic gears are significant for many different applications. In particular, epicyclic gears have higher gear ratios. The reason behind this is that epicyclic gears require multiple mesh considerations. The epicyclic gears are designed to calculate the number of load application cycles per unit time. The sun gear, for example, is +1300 RPM. The planet gear, on the other hand, is +1700 RPM. The ring gear is also +1400 RPM, as determined by the number of teeth in each gear.
Torque is the twisting force of a gear, and the bigger the gear, the higher the torque. However, since the torque is also proportional to the size of the gear, bigger radii result in lower torque. In addition, smaller radii do not move cars faster, so the higher gear ratios do not move at highway speeds. The tradeoff between speed and torque is the gear ratio.
Planetary gears use multiple mechanisms to increase the gear ratio. Those using epicyclic gears have multiple gear sets, including a sun, a ring, and two planets. Moreover, the planetary gears are based on helical, bevel, and spur gears. In general, the higher gear ratios of epicyclic gears are superior to those of planetary gears.
Another example of planetary gears is the compound planet. This gear design has two different-sized gears on either end of a common casting. The large end engages the sun while the smaller end engages the annulus. The compound planets are sometimes necessary to achieve smaller steps in gear ratio. As with any gear, the correct alignment of planet pins is essential for proper operation. If the planets are not aligned properly, it may result in rough running or premature breakdown.


editor by Cx2023-07-13
China 1325 Plasma Cutting rack #45 Steel Mod 1.5 2 3 4 5 6 8 10 Rack And Pinion Helical GEAR Rack rack gear examples
Condition: New
Warranty: 6 Months
Shape: Rack Gear
Applicable Industries: Manufacturing Plant, lift, elevator, escalator, medical device
Weight (KG): 4.5
Showroom Location: Turkey, India, None
Video outgoing-inspection: Provided
Machinery Test Report: Provided
Marketing Type: Ordinary Product
Warranty of core components: 1 Year
Core Components: Gear
Model Number: 1.5CHR1006
Material: Steel
Processing: Hobbing
Standard or Nonstandard: Standard
Module: 1.5-10
Heat Treatment: Tooth surface induction hardened
Teeth Type: Helical
Quality: DIN6 DIN7 DIN9
Surface treatment: Ground
Packaging Details: shrink film and wooden case
Port: HangZhou Shangahi
Gear Rack Description
| Standard Module 1.5 Helical Gear Rack Specificaiton | ||||||
| Item No. | 1.5CHR1006 | 1.5CQR1007 | 1.5CHR1009 | |||
| Precision grade | DIN6 | DIN7 | DIN9 | |||
| Tooth hardness | 50-55HRC | 15-20HRC | 50-55HRC | |||
| Surface Treatment | Ground | Ground | Ground | |||
| Heat Treatment | Induction hardened | Quenched | Induciton hardened | |||
| Right hand angel | 19°31′42″ | 19°31′42″ | 19°31′42″ Iced out bling CZPT hip hop miami wholesale cuban link chain jewelry moissanite cuban chain | |||
| Pressure angle | 20° | 20° | 20° | |||

Spiral Gears for Right-Angle Right-Hand Drives
Spiral gears are used in mechanical systems to transmit torque. The bevel gear is a particular type of spiral gear. It is made up of two gears that mesh with one another. Both gears are connected by a bearing. The two gears must be in mesh alignment so that the negative thrust will push them together. If axial play occurs in the bearing, the mesh will have no backlash. Moreover, the design of the spiral gear is based on geometrical tooth forms.
Equations for spiral gear
The theory of divergence requires that the pitch cone radii of the pinion and gear be skewed in different directions. This is done by increasing the slope of the convex surface of the gear’s tooth and decreasing the slope of the concave surface of the pinion’s tooth. The pinion is a ring-shaped wheel with a central bore and a plurality of transverse axes that are offset from the axis of the spiral teeth.
Spiral bevel gears have a helical tooth flank. The spiral is consistent with the cutter curve. The spiral angle b is equal to the pitch cone’s genatrix element. The mean spiral angle bm is the angle between the genatrix element and the tooth flank. The equations in Table 2 are specific for the Spread Blade and Single Side gears from Gleason.
The tooth flank equation of a logarithmic spiral bevel gear is derived using the formation mechanism of the tooth flanks. The tangential contact force and the normal pressure angle of the logarithmic spiral bevel gear were found to be about twenty degrees and 35 degrees respectively. These two types of motion equations were used to solve the problems that arise in determining the transmission stationary. While the theory of logarithmic spiral bevel gear meshing is still in its infancy, it does provide a good starting point for understanding how it works.
This geometry has many different solutions. However, the main two are defined by the root angle of the gear and pinion and the diameter of the spiral gear. The latter is a difficult one to constrain. A 3D sketch of a bevel gear tooth is used as a reference. The radii of the tooth space profile are defined by end point constraints placed on the bottom corners of the tooth space. Then, the radii of the gear tooth are determined by the angle.
The cone distance Am of a spiral gear is also known as the tooth geometry. The cone distance should correlate with the various sections of the cutter path. The cone distance range Am must be able to correlate with the pressure angle of the flanks. The base radii of a bevel gear need not be defined, but this geometry should be considered if the bevel gear does not have a hypoid offset. When developing the tooth geometry of a spiral bevel gear, the first step is to convert the terminology to pinion instead of gear.
The normal system is more convenient for manufacturing helical gears. In addition, the helical gears must be the same helix angle. The opposite hand helical gears must mesh with each other. Likewise, the profile-shifted screw gears need more complex meshing. This gear pair can be manufactured in a similar way to a spur gear. Further, the calculations for the meshing of helical gears are presented in Table 7-1.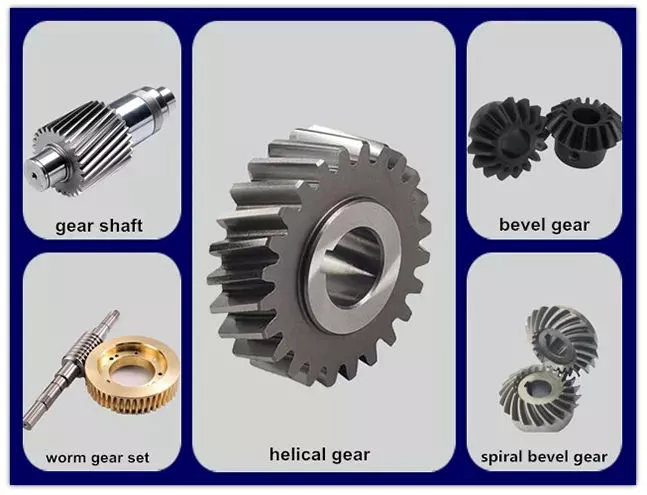
Design of spiral bevel gears
A proposed design of spiral bevel gears utilizes a function-to-form mapping method to determine the tooth surface geometry. This solid model is then tested with a surface deviation method to determine whether it is accurate. Compared to other right-angle gear types, spiral bevel gears are more efficient and compact. CZPT Gear Company gears comply with AGMA standards. A higher quality spiral bevel gear set achieves 99% efficiency.
A geometric meshing pair based on geometric elements is proposed and analyzed for spiral bevel gears. This approach can provide high contact strength and is insensitive to shaft angle misalignment. Geometric elements of spiral bevel gears are modeled and discussed. Contact patterns are investigated, as well as the effect of misalignment on the load capacity. In addition, a prototype of the design is fabricated and rolling tests are conducted to verify its accuracy.
The three basic elements of a spiral bevel gear are the pinion-gear pair, the input and output shafts, and the auxiliary flank. The input and output shafts are in torsion, the pinion-gear pair is in torsional rigidity, and the system elasticity is small. These factors make spiral bevel gears ideal for meshing impact. To improve meshing impact, a mathematical model is developed using the tool parameters and initial machine settings.
In recent years, several advances in manufacturing technology have been made to produce high-performance spiral bevel gears. Researchers such as Ding et al. optimized the machine settings and cutter blade profiles to eliminate tooth edge contact, and the result was an accurate and large spiral bevel gear. In fact, this process is still used today for the manufacturing of spiral bevel gears. If you are interested in this technology, you should read on!
The design of spiral bevel gears is complex and intricate, requiring the skills of expert machinists. Spiral bevel gears are the state of the art for transferring power from one system to another. Although spiral bevel gears were once difficult to manufacture, they are now common and widely used in many applications. In fact, spiral bevel gears are the gold standard for right-angle power transfer.While conventional bevel gear machinery can be used to manufacture spiral bevel gears, it is very complex to produce double bevel gears. The double spiral bevel gearset is not machinable with traditional bevel gear machinery. Consequently, novel manufacturing methods have been developed. An additive manufacturing method was used to create a prototype for a double spiral bevel gearset, and the manufacture of a multi-axis CNC machine center will follow.
Spiral bevel gears are critical components of helicopters and aerospace power plants. Their durability, endurance, and meshing performance are crucial for safety. Many researchers have turned to spiral bevel gears to address these issues. One challenge is to reduce noise, improve the transmission efficiency, and increase their endurance. For this reason, spiral bevel gears can be smaller in diameter than straight bevel gears. If you are interested in spiral bevel gears, check out this article.
Limitations to geometrically obtained tooth forms
The geometrically obtained tooth forms of a spiral gear can be calculated from a nonlinear programming problem. The tooth approach Z is the linear displacement error along the contact normal. It can be calculated using the formula given in Eq. (23) with a few additional parameters. However, the result is not accurate for small loads because the signal-to-noise ratio of the strain signal is small.
Geometrically obtained tooth forms can lead to line and point contact tooth forms. However, they have their limits when the tooth bodies invade the geometrically obtained tooth form. This is called interference of tooth profiles. While this limit can be overcome by several other methods, the geometrically obtained tooth forms are limited by the mesh and strength of the teeth. They can only be used when the meshing of the gear is adequate and the relative motion is sufficient.
During the tooth profile measurement, the relative position between the gear and the LTS will constantly change. The sensor mounting surface should be parallel to the rotational axis. The actual orientation of the sensor may differ from this ideal. This may be due to geometrical tolerances of the gear shaft support and the platform. However, this effect is minimal and is not a serious problem. So, it is possible to obtain the geometrically obtained tooth forms of spiral gear without undergoing expensive experimental procedures.
The measurement process of geometrically obtained tooth forms of a spiral gear is based on an ideal involute profile generated from the optical measurements of one end of the gear. This profile is assumed to be almost perfect based on the general orientation of the LTS and the rotation axis. There are small deviations in the pitch and yaw angles. Lower and upper bounds are determined as – 10 and -10 degrees respectively.
The tooth forms of a spiral gear are derived from replacement spur toothing. However, the tooth shape of a spiral gear is still subject to various limitations. In addition to the tooth shape, the pitch diameter also affects the angular backlash. The values of these two parameters vary for each gear in a mesh. They are related by the transmission ratio. Once this is understood, it is possible to create a gear with a corresponding tooth shape.
As the length and transverse base pitch of a spiral gear are the same, the helix angle of each profile is equal. This is crucial for engagement. An imperfect base pitch results in an uneven load sharing between the gear teeth, which leads to higher than nominal loads in some teeth. This leads to amplitude modulated vibrations and noise. In addition, the boundary point of the root fillet and involute could be reduced or eliminate contact before the tip diameter.


editor by Cx2023-07-07
China China good price 4 Axis cnc router gear rack brackets
Situation: New
Positioning Accuracy (mm): .03 mm
Number of Axes: four
No. of Spindles: ATC
Working Desk Measurement(mm): 1300×2500
Device Type: CNC Router
Vacation (X Axis)(mm): 1300 mm
Travel (Y Axis)(mm): 2500 mm
Repeatability (X/Y/Z) (mm): 400 mm
CNC or Not: CNC
Voltage: 380V
Dimension(L*W*H): 4000*2250*2250mm
Weight (KG): 1800
Guarantee: 18months
Essential Marketing Factors: Multifunctional
Applicable Industries: Accommodations, Garment Shops, Building Material Shops, Equipment Mend Outlets, Manufacturing Plant, Foodstuff & Beverage Manufacturing unit, Farms, Cafe, Property Use, Retail, Food Store, Printing Outlets, Design works , Energy & Mining, Food & Beverage Shops, Marketing Firm
4 Axis CNC Router Spindle: 2.2kw 5.5kw 7kw 9kw
Solution identify: 1325 4axis Cnc Milling Equipment 3d Statues Creating Router
4 Axis CNC Router Motor and Driver: Stepper or Servo(China manufacturer or Japan Brand)
four Axis CNC Router Transmission: ZheJiang Hiwin Linear Square Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Rail
four Axis CNCRouter Driveing Method: Germany Equipment Rack
four Axis CNC Router Handle System: Syntec/Siemens
four Axis CNC Router Inverter: Delta/Yakskawa
4 Axis CNC Router Application: Woodworking Enrgaving/Slicing
Keywords and phrases: 4 Axis 3d Statues Producing Device
Other Identify: 3d Statues Creating Router
Packaging Particulars: Normal woodes instances packaging for exporting
China great value Multi head 4 axis rotary 8 heads cylinder cnc router Features1.Working dimensions:1300*2500*400mm,C axis:
Click on listed here for far more informationes
Types of Bevel Gears
Bevel Gears are used in a number of industries. They are used in wheeled excavators, dredges, conveyor belts, mill actuators, and rail transmissions. A bevel gear’s spiral or angled bevel can make it suitable for confined spaces. It is also used in robotics and vertical supports of rolling mills. You can use bevel gears in food processing processes. For more information on bevel gears, read on.
Spiral bevel gear
Spiral bevel gears are used to transmit power between two shafts in a 90-degree orientation. They have curved or oblique teeth and can be fabricated from various metals. Bestagear is one manufacturer specializing in medium to large spiral bevel gears. They are used in the mining, metallurgical, marine, and oil fields. Spiral bevel gears are usually made from steel, aluminum, or phenolic materials.
Spiral bevel gears have many advantages. Their mesh teeth create a less abrupt force transfer. They are incredibly durable and are designed to last a long time. They are also less expensive than other right-angle gears. They also tend to last longer, because they are manufactured in pairs. The spiral bevel gear also reduces noise and vibration from its counterparts. Therefore, if you are in need of a new gear set, spiral bevel gears are the right choice.
The contact between spiral bevel gear teeth occurs along the surface of the gear tooth. The contact follows the Hertz theory of elastic contact. This principle holds for small significant dimensions of the contact area and small relative radii of curvature of the surfaces. In this case, strains and friction are negligible. A spiral bevel gear is a common example of an inverted helical gear. This gear is commonly used in mining equipment.
Spiral bevel gears also have a backlash-absorbing feature. This feature helps secure the thickness of the oil film on the gear surface. The shaft axis, mounting distance, and angle errors all affect the tooth contact on a spiral bevel gear. Adjusting backlash helps to correct these problems. The tolerances shown above are common for bevel gears. In some cases, manufacturers make slight design changes late in the production process, which minimizes the risk to OEMs.
Straight bevel gear
Straight bevel gears are among the easiest types of gears to manufacture. The earliest method used to manufacture straight bevel gears was to use a planer equipped with an indexing head. However, improvements have been made in manufacturing methods after the introduction of the Revacycle system and the Coniflex. The latest technology allows for even more precise manufacturing. Both of these manufacturing methods are used by CZPT. Here are some examples of straight bevel gear manufacturing.
A straight bevel gear is manufactured using two kinds of bevel surfaces, namely, the Gleason method and the Klingelnberg method. Among the two, the Gleason method is the most common. Unlike other types of gear, the CZPT method is not a universal standard. The Gleason system has higher quality gears, since its adoption of tooth crowning is the most effective way to make gears that tolerate even small assembly errors. It also eliminates the stress concentration in the bevelled edges of the teeth.
The gear’s composition depends on the application. When durability is required, a gear is made of cast iron. The pinion is usually three times harder than the gear, which helps balance wear. Other materials, such as carbon steel, are cheaper, but are less resistant to corrosion. Inertia is another critical factor to consider, since heavier gears are more difficult to reverse and stop. Precision requirements may include the gear pitch and diameter, as well as the pressure angle.
Involute geometry of a straight bevel gear is often computed by varying the surface’s normal to the surface. Involute geometry is computed by incorporating the surface coordinates and the theoretical tooth thickness. Using the CMM, the spherical involute surface can be used to determine tooth contact patterns. This method is useful when a roll tester tooling is unavailable, because it can predict the teeth’ contact pattern.
Hypoid bevel gear
Hypoid bevel gears are an efficient and versatile speed reduction solution. Their compact size, high efficiency, low noise and heat generation, and long life make them a popular choice in the power transmission and motion control industries. The following are some of the benefits of hypoid gearing and why you should use it. Listed below are some of the key misperceptions and false assumptions of this gear type. These assumptions may seem counterintuitive at first, but will help you understand what this gear is all about.
The basic concept of hypoid gears is that they use two non-intersecting shafts. The smaller gear shaft is offset from the larger gear shaft, allowing them to mesh without interference and support each other securely. The resulting torque transfer is improved when compared to conventional gear sets. A hypoid bevel gear is used to drive the rear axle of an automobile. It increases the flexibility of machine design and allows the axes to be freely adjusted.
In the first case, the mesh of the two bodies is obtained by fitting the hyperboloidal cutter to the desired gear. Its geometric properties, orientation, and position determine the desired gear. The latter is used if the desired gear is noise-free or is required to reduce vibrations. A hyperboloidal cutter, on the other hand, meshes with two toothed bodies. It is the most efficient option for modeling hypoid gears with noise concerns.
The main difference between hypoid and spiral bevel gears is that the hypoid bevel gear has a larger diameter than its counterparts. They are usually found in 1:1 and 2:1 applications, but some manufacturers also provide higher ratios. A hypoid gearbox can achieve speeds of three thousand rpm. This makes it the preferred choice in a variety of applications. So, if you’re looking for a gearbox with a high efficiency, this is the gear for you.
Addendum and dedendum angles
The addendum and dedendum angles of a bevel gear are used to describe the shape and depth of the teeth of the gear. Each tooth of the gear has a slightly tapered surface that changes in depth. These angles are defined by their addendum and dedendum distances. Addendum angle is the distance between the top land and the bottom surface of the teeth, while dedendum angle is the distance between the pitch surface and the bottom surface of the teeth.
The pitch angle is the angle formed by the apex point of the gear’s pitch cone with the pitch line of the gear shaft. The dedendum angle, on the other hand, is the depth of the tooth space below the pitch line. Both angles are used to measure the shape of a bevel gear. The addendum and dedendum angles are important for gear design.
The dedendum and addendum angles of a bevel gear are determined by the base contact ratio (Mc) of the two gears. The involute curve is not allowed to extend within the base diameter of the bevel gear. The base diameter is also a critical measurement for the design of a gear. It is possible to reduce the involute curve to match the involute curve, but it must be tangential to the involute curve.
The most common application of a bevel gear is the automotive differential. They are used in many types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, and even construction equipment. They are also used in the marine industry and aviation. Aside from these two common uses, there are many other uses for bevel gears. And they are still growing in popularity. But they’re a valuable part of automotive and industrial gearing systems.
Applications of bevel gears
Bevel gears are used in a variety of applications. They are made of various materials depending on their weight, load, and application. For high-load applications, ferrous metals such as grey cast iron are used. These materials have excellent wear resistance and are inexpensive. For lower-weight applications, steel or non-metals such as plastics are used. Some bevel gear materials are considered noiseless. Here are some of their most common uses.
Straight bevel gears are the easiest to manufacture. The earliest method of manufacturing them was with a planer with an indexing head. Modern manufacturing methods introduced the Revacycle and Coniflex systems. For industrial gear manufacturing, the CZPT uses the Revacycle system. However, there are many types of bevel gears. This guide will help you choose the right material for your next project. These materials can withstand high rotational speeds and are very strong.
Bevel gears are most common in automotive and industrial machinery. They connect the driveshaft to the wheels. Some even have a 45-degree bevel. These gears can be placed on a bevel surface and be tested for their transmission capabilities. They are also used in testing applications to ensure proper motion transmission. They can reduce the speed of straight shafts. Bevel gears can be used in many industries, from marine to aviation.
The simplest type of bevel gear is the miter gear, which has a 1:1 ratio. It is used to change the axis of rotation. The shafts of angular miter bevel gears can intersect at any angle, from 45 degrees to 120 degrees. The teeth on the bevel gear can be straight, spiral, or Zerol. And as with the rack and pinion gears, there are different types of bevel gears.


editor by czh2023-02-20
China 1325 plasma cutting #45 steel mod 1.5 2 3 4 5 6 8 10 rack and pinion helical rack gear rack backlash
Issue: New
Warranty: 1.5 many years
Form: Rack Equipment
Applicable Industries: Accommodations, Garment Retailers, Developing Content Retailers, Manufacturing Plant, Equipment Restore Retailers, Meals & Beverage Manufacturing facility, Farms, Cafe, Construction works , Power & Mining, Other, Advertising Organization
Weight (KG): 10
Showroom Spot: None
Movie outgoing-inspection: Supplied
Equipment Examination Report: Offered
Advertising Type: New Item 2571
Warranty of core elements: 1 Calendar year
Core Parts: Equipment
Design Amount: personalized
Content: Steel
Processing: Hobbing
Regular or Nonstandard: Normal
Solution name: CNC Tailored Equipment Rack
Tooth Profile: Helical Teeth
Application: Industry Machinery
Title: C45 Steel Helical Cnc Equipment Racks
Tooth Variety: StraightHelical
Use: Machine Generate
Size: Personalized Duration
Payment Phrase: T/T
Colour: Customers’ Calls for
Floor treatment: Polished
Packaging Details: Wooden box
Port: HangZhou
Specification
| item | value |
| Condition | New |
| Warranty | 1.5 many years |
| Shape | Rack Gear |
| Applicable Industries | Hotels, Garment Stores, Creating Substance Stores, Producing Plant, Machinery Mend Stores, Foods & Beverage Manufacturing unit, Transmission Reducer 38 211z 6-Hole Excess fat Lowering Velocity Reducer Washing Device Gear Box Motor Gearbox Element For Lg Haier Price tag Farms, Restaurant, Building functions , Vitality & Mining, Other, Advertising Firm |
| Weight (KG) | 10 |
| Showroom Place | None |
| Video outgoing-inspection | Provided |
| Machinery Examination Report | Provided |
| Marketing Variety | New Item 2571 |
| Warranty of main components | 1 12 months |
| Core Parts | Gear |
| Place of Origin | China |
| ZheJiang | |
| Model Quantity | customized |
| Brand Title | youteng |
| Material | Steel |
| Processing | Hobbing |
| Standard or Nonstandard | Standard |
| Product name | CNC Customized Equipment Rack |
| Tooth Profile | Helical Tooth |
| Application | Industry Machinery |
| Name | C45 Steel Helical Cnc Equipment Racks |
| Teeth Sort | StraightHelical |
| Usage | Machine Travel |
| Length | Customized Size |
| Payment Time period | T/T |
| Color | Customers’ Calls for |
| Surface treatment | Polished |
How to Compare Different Types of Spur Gears
When comparing different types of spur gears, there are several important considerations to take into account. The main considerations include the following: Common applications, Pitch diameter, and Addendum circle. Here we will look at each of these factors in more detail. This article will help you understand what each type of spur gear can do for you. Whether you’re looking to power an electric motor or a construction machine, the right gear for the job will make the job easier and save you money in the long run.
Common applications
Among its many applications, a spur gear is widely used in airplanes, trains, and bicycles. It is also used in ball mills and crushers. Its high speed-low torque capabilities make it ideal for a variety of applications, including industrial machines. The following are some of the common uses for spur gears. Listed below are some of the most common types. While spur gears are generally quiet, they do have their limitations.
A spur gear transmission can be external or auxiliary. These units are supported by front and rear casings. They transmit drive to the accessory units, which in turn move the machine. The drive speed is typically between 5000 and 6000 rpm or 20,000 rpm for centrifugal breathers. For this reason, spur gears are typically used in large machinery. To learn more about spur gears, watch the following video.
The pitch diameter and diametral pitch of spur gears are important parameters. A diametral pitch, or ratio of teeth to pitch diameter, is important in determining the center distance between two spur gears. The center distance between two spur gears is calculated by adding the radius of each pitch circle. The addendum, or tooth profile, is the height by which a tooth projects above the pitch circle. Besides pitch, the center distance between two spur gears is measured in terms of the distance between their centers.
Another important feature of a spur gear is its low speed capability. It can produce great power even at low speeds. However, if noise control is not a priority, a helical gear is preferable. Helical gears, on the other hand, have teeth arranged in the opposite direction of the axis, making them quieter. However, when considering the noise level, a helical gear will work better in low-speed situations.
Construction
The construction of spur gear begins with the cutting of the gear blank. The gear blank is made of a pie-shaped billet and can vary in size, shape, and weight. The cutting process requires the use of dies to create the correct gear geometry. The gear blank is then fed slowly into the screw machine until it has the desired shape and size. A steel gear blank, called a spur gear billet, is used in the manufacturing process.
A spur gear consists of two parts: a centre bore and a pilot hole. The addendum is the circle that runs along the outermost points of a spur gear’s teeth. The root diameter is the diameter at the base of the tooth space. The plane tangent to the pitch surface is called the pressure angle. The total diameter of a spur gear is equal to the addendum plus the dedendum.
The pitch circle is a circle formed by a series of teeth and a diametrical division of each tooth. The pitch circle defines the distance between two meshed gears. The center distance is the distance between the gears. The pitch circle diameter is a crucial factor in determining center distances between two mating spur gears. The center distance is calculated by adding the radius of each gear’s pitch circle. The dedendum is the height of a tooth above the pitch circle.
Other considerations in the design process include the material used for construction, surface treatments, and number of teeth. In some cases, a standard off-the-shelf gear is the most appropriate choice. It will meet your application needs and be a cheaper alternative. The gear will not last for long if it is not lubricated properly. There are a number of different ways to lubricate a spur gear, including hydrodynamic journal bearings and self-contained gears.
Addendum circle
The pitch diameter and addendum circle are two important dimensions of a spur gear. These diameters are the overall diameter of the gear and the pitch circle is the circle centered around the root of the gear’s tooth spaces. The addendum factor is a function of the pitch circle and the addendum value, which is the radial distance between the top of the gear tooth and the pitch circle of the mating gear.
The pitch surface is the right-hand side of the pitch circle, while the root circle defines the space between the two gear tooth sides. The dedendum is the distance between the top of the gear tooth and the pitch circle, and the pitch diameter and addendum circle are the two radial distances between these two circles. The difference between the pitch surface and the addendum circle is known as the clearance.
The number of teeth in the spur gear must not be less than 16 when the pressure angle is twenty degrees. However, a gear with 16 teeth can still be used if its strength and contact ratio are within design limits. In addition, undercutting can be prevented by profile shifting and addendum modification. However, it is also possible to reduce the addendum length through the use of a positive correction. However, it is important to note that undercutting can happen in spur gears with a negative addendum circle.
Another important aspect of a spur gear is its meshing. Because of this, a standard spur gear will have a meshing reference circle called a Pitch Circle. The center distance, on the other hand, is the distance between the center shafts of the two gears. It is important to understand the basic terminology involved with the gear system before beginning a calculation. Despite this, it is essential to remember that it is possible to make a spur gear mesh using the same reference circle.
Pitch diameter
To determine the pitch diameter of a spur gear, the type of drive, the type of driver, and the type of driven machine should be specified. The proposed diametral pitch value is also defined. The smaller the pitch diameter, the less contact stress on the pinion and the longer the service life. Spur gears are made using simpler processes than other types of gears. The pitch diameter of a spur gear is important because it determines its pressure angle, the working depth, and the whole depth.
The ratio of the pitch diameter and the number of teeth is called the DIAMETRAL PITCH. The teeth are measured in the axial plane. The FILLET RADIUS is the curve that forms at the base of the gear tooth. The FULL DEPTH TEETH are the ones with the working depth equal to 2.000 divided by the normal diametral pitch. The hub diameter is the outside diameter of the hub. The hub projection is the distance the hub extends beyond the gear face.
A metric spur gear is typically specified with a Diametral Pitch. This is the number of teeth per inch of the pitch circle diameter. It is generally measured in inverse inches. The normal plane intersects the tooth surface at the point where the pitch is specified. In a helical gear, this line is perpendicular to the pitch cylinder. In addition, the pitch cylinder is normally normal to the helix on the outside.
The pitch diameter of a spur gear is typically specified in millimeters or inches. A keyway is a machined groove on the shaft that fits the key into the shaft’s keyway. In the normal plane, the pitch is specified in inches. Involute pitch, or diametral pitch, is the ratio of teeth per inch of diameter. While this may seem complicated, it’s an important measurement to understand the pitch of a spur gear.
Material
The main advantage of a spur gear is its ability to reduce the bending stress at the tooth no matter the load. A typical spur gear has a face width of 20 mm and will fail when subjected to 3000 N. This is far more than the yield strength of the material. Here is a look at the material properties of a spur gear. Its strength depends on its material properties. To find out what spur gear material best suits your machine, follow the following steps.
The most common material used for spur gears is steel. There are different kinds of steel, including ductile iron and stainless steel. S45C steel is the most common steel and has a 0.45% carbon content. This type of steel is easily obtainable and is used for the production of helical, spur, and worm gears. Its corrosion resistance makes it a popular material for spur gears. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of steel.
A spur gear is made of metal, plastic, or a combination of these materials. The main advantage of metal spur gears is their strength to weight ratio. It is about one third lighter than steel and resists corrosion. While aluminum is more expensive than steel and stainless steel, it is also easier to machine. Its design makes it easy to customize for the application. Its versatility allows it to be used in virtually every application. So, if you have a specific need, you can easily find a spur gear that fits your needs.
The design of a spur gear greatly influences its performance. Therefore, it is vital to choose the right material and measure the exact dimensions. Apart from being important for performance, dimensional measurements are also important for quality and reliability. Hence, it is essential for professionals in the industry to be familiar with the terms used to describe the materials and parts of a gear. In addition to these, it is essential to have a good understanding of the material and the dimensional measurements of a gear to ensure that production and purchase orders are accurate.


editor by czh2023-02-16
China 4 Eyes Light Nylon Gear Rack gear rack backlash
Item Description
Solution Description
Nylon Gear Rack
produced of nylon and has metal bar inside,utilised for sliding gate.
It normally works with Gate Motor.
We have 2 Eyes Light, 2 Eyes Heavy,4 Eyes Light and 6 Eyes Weighty.
Each piece of nylon gear rack has screws as images display underneath,
Our items are exported to Southeast Asia, Europe, South America, and so on. Reputable quality
You are warmly welcome to deliver us an inquiry for thorough information.
| Solution Title | Specification | Modulus | Substance |
| Nylon Rack | 2 Eyes Mild | M4 | PA66 |
| Nylon Rack | 2 Eyes Large | M4 | PA66 |
| Nylon Rack | 4 Eyes Light-weight | M4 | PA66 |
| Nylon Rack | six Eyes Weighty | M4 | PA66 |
| Iron Rack | 8*thirty*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 8*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | nine*thirty*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 10*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | ten*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 11*thirty*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | eleven*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | twelve*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 12*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 22*22*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 22*22*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | thirty*thirty*998 | M6 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | thirty*30*1998 | M6 | Q235 |
Company Profile
Principal Products
Creation Method
Packaging & Shipping and delivery
FAQ
| Type: | Sliding Door Accessories |
|---|---|
| Material: | Nylon and Iron Steel |
| Modulus: | M4 |
| Delivery: | 2~7 Days for Stock, 15~45 Days for Without Stock |
| Feature: | Oil-Resistant, Corrosion-Resistant, Heat-Resistant |
| Color: | Black |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Product Name | Specification | Modulus | Material |
| Nylon Rack | 2 Eyes Light | M4 | PA66 |
| Nylon Rack | 2 Eyes Heavy | M4 | PA66 |
| Nylon Rack | 4 Eyes Light | M4 | PA66 |
| Nylon Rack | 6 Eyes Heavy | M4 | PA66 |
| Iron Rack | 8*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 8*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 9*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 10*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 10*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 11*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 11*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 12*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 12*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 22*22*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 22*22*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 30*30*998 | M6 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 30*30*1998 | M6 | Q235 |
| Type: | Sliding Door Accessories |
|---|---|
| Material: | Nylon and Iron Steel |
| Modulus: | M4 |
| Delivery: | 2~7 Days for Stock, 15~45 Days for Without Stock |
| Feature: | Oil-Resistant, Corrosion-Resistant, Heat-Resistant |
| Color: | Black |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Product Name | Specification | Modulus | Material |
| Nylon Rack | 2 Eyes Light | M4 | PA66 |
| Nylon Rack | 2 Eyes Heavy | M4 | PA66 |
| Nylon Rack | 4 Eyes Light | M4 | PA66 |
| Nylon Rack | 6 Eyes Heavy | M4 | PA66 |
| Iron Rack | 8*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 8*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 9*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 10*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 10*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 11*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 11*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 12*30*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 12*30*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 22*22*1005 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 22*22*1998 | M4 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 30*30*998 | M6 | Q235 |
| Iron Rack | 30*30*1998 | M6 | Q235 |
Hypoid Bevel Vs Straight Spiral Bevel – What’s the Difference?
Spiral gears come in many different varieties, but there is a fundamental difference between a Hypoid bevel gear and a Straight spiral bevel. This article will describe the differences between the two types of gears and discuss their use. Whether the gears are used in industrial applications or at home, it is vital to understand what each type does and why it is important. Ultimately, your final product will depend on these differences.
Hypoid bevel gears
In automotive use, hypoid bevel gears are used in the differential, which allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while maintaining the vehicle’s handling. This gearbox assembly consists of a ring gear and pinion mounted on a carrier with other bevel gears. These gears are also widely used in heavy equipment, auxiliary units, and the aviation industry. Listed below are some common applications of hypoid bevel gears.
For automotive applications, hypoid gears are commonly used in rear axles, especially on large trucks. Their distinctive shape allows the driveshaft to be located deeper in the vehicle, thus lowering the center of gravity and minimizing interior disruption. This design makes the hypoid gearset one of the most efficient types of gearboxes on the market. In addition to their superior efficiency, hypoid gears are very easy to maintain, as their mesh is based on sliding action.
The face-hobbed hypoid gears have a characteristic epicycloidal lead curve along their lengthwise axis. The most common grinding method for hypoid gears is the Semi-Completing process, which uses a cup-shaped grinding wheel to replace the lead curve with a circular arc. However, this method has a significant drawback – it produces non-uniform stock removal. Furthermore, the grinding wheel cannot finish all the surface of the tooth.
The advantages of a hypoid gear over a spiral bevel gear include a higher contact ratio and a higher transmission torque. These gears are primarily used in automobile drive systems, where the ratio of a single pair of hypoid gears is the highest. The hypoid gear can be heat-treated to increase durability and reduce friction, making it an ideal choice for applications where speed and efficiency are critical.
The same technique used in spiral bevel gears can also be used for hypoid bevel gears. This machining technique involves two-cut roughing followed by one-cut finishing. The pitch diameter of hypoid gears is up to 2500 mm. It is possible to combine the roughing and finishing operations using the same cutter, but the two-cut machining process is recommended for hypoid gears.
The advantages of hypoid gearing over spiral bevel gears are primarily based on precision. Using a hypoid gear with only three arc minutes of backlash is more efficient than a spiral bevel gear that requires six arc minutes of backlash. This makes hypoid gears a more viable choice in the motion control market. However, some people may argue that hypoid gears are not practical for automobile assemblies.
Hypoid gears have a unique shape – a cone that has teeth that are not parallel. Their pitch surface consists of two surfaces – a conical surface and a line-contacting surface of revolution. An inscribed cone is a common substitute for the line-contact surface of hypoid bevel gears, and it features point-contacts instead of lines. Developed in the early 1920s, hypoid bevel gears are still used in heavy truck drive trains. As they grow in popularity, they are also seeing increasing use in the industrial power transmission and motion control industries.
Straight spiral bevel gears
There are many differences between spiral bevel gears and the traditional, non-spiral types. Spiral bevel gears are always crowned and never conjugated, which limits the distribution of contact stress. The helical shape of the bevel gear is also a factor of design, as is its length. The helical shape has a large number of advantages, however. Listed below are a few of them.
Spiral bevel gears are generally available in pitches ranging from 1.5 to 2500 mm. They are highly efficient and are also available in a wide range of tooth and module combinations. Spiral bevel gears are extremely accurate and durable, and have low helix angles. These properties make them excellent for precision applications. However, some gears are not suitable for all applications. Therefore, you should consider the type of bevel gear you need before purchasing.
Compared to helical gears, straight bevel gears are easier to manufacture. The earliest method used to manufacture these gears was the use of a planer with an indexing head. However, with the development of modern manufacturing processes such as the Revacycle and Coniflex systems, manufacturers have been able to produce these gears more efficiently. Some of these gears are used in windup alarm clocks, washing machines, and screwdrivers. However, they are particularly noisy and are not suitable for automobile use.
A straight bevel gear is the most common type of bevel gear, while a spiral bevel gear has concave teeth. This curved design produces a greater amount of torque and axial thrust than a straight bevel gear. Straight teeth can increase the risk of breaking and overheating equipment and are more prone to breakage. Spiral bevel gears are also more durable and last longer than helical gears.
Spiral and hypoid bevel gears are used for applications with high peripheral speeds and require very low friction. They are recommended for applications where noise levels are essential. Hypoid gears are suitable for applications where they can transmit high torque, although the helical-spiral design is less effective for braking. For this reason, spiral bevel gears and hypoids are generally more expensive. If you are planning to buy a new gear, it is important to know which one will be suitable for the application.
Spiral bevel gears are more expensive than standard bevel gears, and their design is more complex than that of the spiral bevel gear. However, they have the advantage of being simpler to manufacture and are less likely to produce excessive noise and vibration. They also have less teeth to grind, which means that they are not as noisy as the spiral bevel gears. The main benefit of this design is their simplicity, as they can be produced in pairs, which saves money and time.
In most applications, spiral bevel gears have advantages over their straight counterparts. They provide more evenly distributed tooth loads and carry more load without surface fatigue. The spiral angle of the teeth also affects thrust loading. It is possible to make a straight spiral bevel gear with two helical axes, but the difference is the amount of thrust that is applied to each individual tooth. In addition to being stronger, the spiral angle provides the same efficiency as the straight spiral gear.
Hypoid gears
The primary application of hypoid gearboxes is in the automotive industry. They are typically found on the rear axles of passenger cars. The name is derived from the left-hand spiral angle of the pinion and the right-hand spiral angle of the crown. Hypoid gears also benefit from an offset center of gravity, which reduces the interior space of cars. Hypoid gears are also used in heavy trucks and buses, where they can improve fuel efficiency.
The hypoid and spiral bevel gears can be produced by face-hobbing, a process that produces highly accurate and smooth-surfaced parts. This process enables precise flank surfaces and pre-designed ease-off topographies. These processes also enhance the mechanical resistance of the gears by 15 to 20%. Additionally, they can reduce noise and improve mechanical efficiency. In commercial applications, hypoid gears are ideal for ensuring quiet operation.
Conjugated design enables the production of hypoid gearsets with length or profile crowning. Its characteristic makes the gearset insensitive to inaccuracies in the gear housing and load deflections. In addition, crowning allows the manufacturer to adjust the operating displacements to achieve the desired results. These advantages make hypoid gear sets a desirable option for many industries. So, what are the advantages of hypoid gears in spiral gears?
The design of a hypoid gear is similar to that of a conventional bevel gear. Its pitch surfaces are hyperbolic, rather than conical, and the teeth are helical. This configuration also allows the pinion to be larger than an equivalent bevel pinion. The overall design of the hypoid gear allows for large diameter shafts and a large pinion. It can be considered a cross between a bevel gear and a worm drive.
In passenger vehicles, hypoid gears are almost universal. Their smoother operation, increased pinion strength, and reduced weight make them a desirable choice for many vehicle applications. And, a lower vehicle body also lowers the vehicle’s body. These advantages made all major car manufacturers convert to hypoid drive axles. It is worth noting that they are less efficient than their bevel gear counterparts.
The most basic design characteristic of a hypoid gear is that it carries out line contact in the entire area of engagement. In other words, if a pinion and a ring gear rotate with an angular increment, line contact is maintained throughout their entire engagement area. The resulting transmission ratio is equal to the angular increments of the pinion and ring gear. Therefore, hypoid gears are also known as helical gears.


editor by czh 2023-01-20
China DIN Standard Gears & Racks Mod. 4 circular gear rack
Product Description
XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.HUA Chain Group is the most professional company of electricity transmission in China, production roller chains, business sprockets, bike sprockets, casting sprockets, diverse type of couplings, pulleys, taper bushes, locking gadgets, gears, shafts, CNC precision parts and so on. We have passed ISO9001, ISO14001, TS16949 this kind of good quality and enviroment certification.
Item DESCRIPITION
Rack and equipment matched together
Mould ( M0.5 — M8)
Length: 250mmr to 3000mm
Standard and special rack
C45 steel/40Cr metal
Znic portray
Note:
1)The racks are of the adhering to characters of high precision:
two)In the entire size of 2000mm, unstraight diploma is inside of .20mm, no subject the measurement is taken at any place of the rack.
three)Tolerance on sum of pitches +/-30μ M on five hundred mm
four)The good quality grade of the toothing is from 8 to 9 at DIN 3962/63/sixty seven
five)Straight toothing
6)Mistake extra up to circumferential pitch of any tooth is considerably less than .20mm
| Prossure angle 20°Material C45 | |||||||||||
| Mod. | Hp | HexS | L | ||||||||
| 500 | 1000 | 2000 | |||||||||
| Teeth No. | Lr | Excess weight(kg) | Tooth NO. | Lr | Bodyweight(kg) | Tooth NO. | Lr | Excess weight(kg) | |||
| one | fourteen | 15×15 | 159 | 449.fifty one | .eighty two | 318 | 999.02 | 1.50 | 636 | 1998.05 | 3.10 |
| 1.five | 15.5 | 17×17 | 106 | 449.51 | 1.00 | 212 | 999.02 | two.00 | 424 | 1998.05 | four.00 |
| 2 | eighteen | 20×20 | eighty | 502.sixty five | one.forty | 159 | 999.02 | 2.70 | 318 | 1998.05 | five.40 |
| 2.five | 22.five | 25×25 | sixty four | 502.sixty five | two.ten | 127 | 997.45 | 4.thirty | 255 | 2002.seventy seven | 8.sixty |
| three | 27 | 30×30 | fifty three | 499.51 | three.10 | 106 | 999.02 | six.thirty | 212 | 1998.05 | twelve.50 |
| 4 | 21 | 25×25 | forty | 502.65 | 1.80 | eighty | 1005.31 | three.65 | 159 | 1998.05 | 7.thirty |
| 4 | 26 | 30×30 | forty | 502.sixty five | three.05 | eighty | 1005.31 | 6.00 | 159 | 1998.05 | 11.ninety |
| four | 36 | 40×40 | forty | 502.65 | 5.50 | eighty | 1005.31 | eleven.ten | 159 | 1998.05 | 22.00 |
| 5 | 45 | 50X50 | 32 | 502.65 | eight.thirty | 64 | 1005.31 | seventeen.fifty | 128 | 2571.31 | 34.60 |
| 6 | fifty four | 60×60 | 27 | 508.ninety three | 12.sixty five | 53 | 999.02 | twenty five.00 | 106 | 1998.05 | 51.00 |
| eight | 72 | 80X80 | twenty | 502.65 | 21.40 | 40 | 1005.31 | forty two.70 | eighty | 2571.sixty two | eighty five.40 |
| To Be Negotiated | 50 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Prossure angle 20°Material C45 | |||||||||||
| Mod. | Hp | HexS | L | ||||||||
| 500 | 1000 | 2000 | |||||||||
| Teeth No. | Lr | Weight(kg) | Teeth NO. | Lr | Weight(kg) | Teeth NO. | Lr | Weight(kg) | |||
| 1 | 14 | 15×15 | 159 | 449.51 | 0.82 | 318 | 999.02 | 1.50 | 636 | 1998.05 | 3.10 |
| 1.5 | 15.5 | 17×17 | 106 | 449.51 | 1.00 | 212 | 999.02 | 2.00 | 424 | 1998.05 | 4.00 |
| 2 | 18 | 20×20 | 80 | 502.65 | 1.40 | 159 | 999.02 | 2.70 | 318 | 1998.05 | 5.40 |
| 2.5 | 22.5 | 25×25 | 64 | 502.65 | 2.10 | 127 | 997.45 | 4.30 | 255 | 2002.77 | 8.60 |
| 3 | 27 | 30×30 | 53 | 499.51 | 3.10 | 106 | 999.02 | 6.30 | 212 | 1998.05 | 12.50 |
| 4 | 21 | 25×25 | 40 | 502.65 | 1.80 | 80 | 1005.31 | 3.65 | 159 | 1998.05 | 7.30 |
| 4 | 26 | 30×30 | 40 | 502.65 | 3.05 | 80 | 1005.31 | 6.00 | 159 | 1998.05 | 11.90 |
| 4 | 36 | 40×40 | 40 | 502.65 | 5.50 | 80 | 1005.31 | 11.10 | 159 | 1998.05 | 22.00 |
| 5 | 45 | 50X50 | 32 | 502.65 | 8.30 | 64 | 1005.31 | 17.50 | 128 | 2010.31 | 34.60 |
| 6 | 54 | 60×60 | 27 | 508.93 | 12.65 | 53 | 999.02 | 25.00 | 106 | 1998.05 | 51.00 |
| 8 | 72 | 80X80 | 20 | 502.65 | 21.40 | 40 | 1005.31 | 42.70 | 80 | 2010.62 | 85.40 |
###
| To Be Negotiated | 50 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Prossure angle 20°Material C45 | |||||||||||
| Mod. | Hp | HexS | L | ||||||||
| 500 | 1000 | 2000 | |||||||||
| Teeth No. | Lr | Weight(kg) | Teeth NO. | Lr | Weight(kg) | Teeth NO. | Lr | Weight(kg) | |||
| 1 | 14 | 15×15 | 159 | 449.51 | 0.82 | 318 | 999.02 | 1.50 | 636 | 1998.05 | 3.10 |
| 1.5 | 15.5 | 17×17 | 106 | 449.51 | 1.00 | 212 | 999.02 | 2.00 | 424 | 1998.05 | 4.00 |
| 2 | 18 | 20×20 | 80 | 502.65 | 1.40 | 159 | 999.02 | 2.70 | 318 | 1998.05 | 5.40 |
| 2.5 | 22.5 | 25×25 | 64 | 502.65 | 2.10 | 127 | 997.45 | 4.30 | 255 | 2002.77 | 8.60 |
| 3 | 27 | 30×30 | 53 | 499.51 | 3.10 | 106 | 999.02 | 6.30 | 212 | 1998.05 | 12.50 |
| 4 | 21 | 25×25 | 40 | 502.65 | 1.80 | 80 | 1005.31 | 3.65 | 159 | 1998.05 | 7.30 |
| 4 | 26 | 30×30 | 40 | 502.65 | 3.05 | 80 | 1005.31 | 6.00 | 159 | 1998.05 | 11.90 |
| 4 | 36 | 40×40 | 40 | 502.65 | 5.50 | 80 | 1005.31 | 11.10 | 159 | 1998.05 | 22.00 |
| 5 | 45 | 50X50 | 32 | 502.65 | 8.30 | 64 | 1005.31 | 17.50 | 128 | 2010.31 | 34.60 |
| 6 | 54 | 60×60 | 27 | 508.93 | 12.65 | 53 | 999.02 | 25.00 | 106 | 1998.05 | 51.00 |
| 8 | 72 | 80X80 | 20 | 502.65 | 21.40 | 40 | 1005.31 | 42.70 | 80 | 2010.62 | 85.40 |
###
The Difference Between Planetary Gears and Spur Gears
A spur gear is a type of mechanical drive that turns an external shaft. The angular velocity is proportional to the rpm and can be easily calculated from the gear ratio. However, to properly calculate angular velocity, it is necessary to know the number of teeth. Fortunately, there are several different types of spur gears. Here’s an overview of their main features. This article also discusses planetary gears, which are smaller, more robust, and more power-dense.
Planetary gears are a type of spur gear
One of the most significant differences between planetary gears and spurgears is the way that the two share the load. Planetary gears are much more efficient than spurgears, enabling high torque transfer in a small space. This is because planetary gears have multiple teeth instead of just one. They are also suitable for intermittent and constant operation. This article will cover some of the main benefits of planetary gears and their differences from spurgears.
While spur gears are more simple than planetary gears, they do have some key differences. In addition to being more basic, they do not require any special cuts or angles. Moreover, the tooth shape of spur gears is much more complex than those of planetary gears. The design determines where the teeth make contact and how much power is available. However, a planetary gear system will be more efficient if the teeth are lubricated internally.
In a planetary gear, there are three shafts: a sun gear, a planet carrier, and an external ring gear. A planetary gear is designed to allow the motion of one shaft to be arrested, while the other two work simultaneously. In addition to two-shaft operation, planetary gears can also be used in three-shaft operations, which are called temporary three-shaft operations. Temporary three-shaft operations are possible through frictional coupling.
Among the many benefits of planetary gears is their adaptability. As the load is shared between several planet gears, it is easier to switch gear ratios, so you do not need to purchase a new gearbox for every new application. Another major benefit of planetary gears is that they are highly resistant to high shock loads and demanding conditions. This means that they are used in many industries.
They are more robust
An epicyclic gear train is a type of transmission that uses concentric axes for input and output. This type of transmission is often used in vehicles with automatic transmissions, such as a Lamborghini Gallardo. It is also used in hybrid cars. These types of transmissions are also more robust than conventional planetary gears. However, they require more assembly time than a conventional parallel shaft gear.
An epicyclic gearing system has three basic components: an input, an output, and a carrier. The number of teeth in each gear determines the ratio of input rotation to output rotation. In some cases, an epicyclic gear system can be made with two planets. A third planet, known as the carrier, meshes with the second planet and the sun gear to provide reversibility. A ring gear is made of several components, and a planetary gear may contain many gears.
An epicyclic gear train can be built so that the planet gear rolls inside the pitch circle of an outer fixed gear ring, or “annular gear.” In such a case, the curve of the planet’s pitch circle is called a hypocycloid. When epicycle gear trains are used in combination with a sun gear, the planetary gear train is made up of both types. The sun gear is usually fixed, while the ring gear is driven.
Planetary gearing, also known as epicyclic gear, is more durable than other types of transmissions. Because planets are evenly distributed around the sun, they have an even distribution of gears. Because they are more robust, they can handle higher torques, reductions, and overhung loads. They are also more energy-dense and robust. In addition, planetary gearing is often able to be converted to various ratios.
They are more power dense
The planet gear and ring gear of a compound planetary transmission are epicyclic stages. One part of the planet gear meshes with the sun gear, while the other part of the gear drives the ring gear. Coast tooth flanks are used only when the gear drive works in reversed load direction. Asymmetry factor optimization equalizes the contact stress safety factors of a planetary gear. The permissible contact stress, sHPd, and the maximum operating contact stress (sHPc) are equalized by asymmetry factor optimization.
In addition, epicyclic gears are generally smaller and require fewer space than helical ones. They are commonly used as differential gears in speed frames and in looms, where they act as a Roper positive let off. They differ in the amount of overdrive and undergearing ratio they possess. The overdrive ratio varies from fifteen percent to forty percent. In contrast, the undergearing ratio ranges from 0.87:1 to 69%.
The TV7-117S turboprop engine gearbox is the first known application of epicyclic gears with asymmetric teeth. This gearbox was developed by the CZPT Corporation for the Ilyushin Il-114 turboprop plane. The TV7-117S’s gearbox arrangement consists of a first planetary-differential stage with three planet gears and a second solar-type coaxial stage with five planet gears. This arrangement gives epicyclic gears the highest power density.
Planetary gearing is more robust and power-dense than other types of gearing. They can withstand higher torques, reductions, and overhung loads. Their unique self-aligning properties also make them highly versatile in rugged applications. It is also more compact and lightweight. In addition to this, epicyclic gears are easier to manufacture than planetary gears. And as a bonus, they are much less expensive.
They are smaller
Epicyclic gears are small mechanical devices that have a central “sun” gear and one or more outer intermediate gears. These gears are held in a carrier or ring gear and have multiple mesh considerations. The system can be sized and speeded by dividing the required ratio by the number of teeth per gear. This process is known as gearing and is used in many types of gearing systems.
Planetary gears are also known as epicyclic gearing. They have input and output shafts that are coaxially arranged. Each planet contains a gear wheel that meshes with the sun gear. These gears are small and easy to manufacture. Another advantage of epicyclic gears is their robust design. They are easily converted into different ratios. They are also highly efficient. In addition, planetary gear trains can be designed to operate in multiple directions.
Another advantage of epicyclic gearing is their reduced size. They are often used for small-scale applications. The lower cost is associated with the reduced manufacturing time. Epicyclic gears should not be made on N/C milling machines. The epicyclic carrier should be cast and tooled on a single-purpose machine, which has several cutters cutting through material. The epicyclic carrier is smaller than the epicyclic gear.
Epicyclic gearing systems consist of three basic components: an input, an output, and a stationary component. The number of teeth in each gear determines the ratio of input rotation to output rotation. Typically, these gear sets are made of three separate pieces: the input gear, the output gear, and the stationary component. Depending on the size of the input and output gear, the ratio between the two components is greater than half.
They have higher gear ratios
The differences between epicyclic gears and regular, non-epicyclic gears are significant for many different applications. In particular, epicyclic gears have higher gear ratios. The reason behind this is that epicyclic gears require multiple mesh considerations. The epicyclic gears are designed to calculate the number of load application cycles per unit time. The sun gear, for example, is +1300 RPM. The planet gear, on the other hand, is +1700 RPM. The ring gear is also +1400 RPM, as determined by the number of teeth in each gear.
Torque is the twisting force of a gear, and the bigger the gear, the higher the torque. However, since the torque is also proportional to the size of the gear, bigger radii result in lower torque. In addition, smaller radii do not move cars faster, so the higher gear ratios do not move at highway speeds. The tradeoff between speed and torque is the gear ratio.
Planetary gears use multiple mechanisms to increase the gear ratio. Those using epicyclic gears have multiple gear sets, including a sun, a ring, and two planets. Moreover, the planetary gears are based on helical, bevel, and spur gears. In general, the higher gear ratios of epicyclic gears are superior to those of planetary gears.
Another example of planetary gears is the compound planet. This gear design has two different-sized gears on either end of a common casting. The large end engages the sun while the smaller end engages the annulus. The compound planets are sometimes necessary to achieve smaller steps in gear ratio. As with any gear, the correct alignment of planet pins is essential for proper operation. If the planets are not aligned properly, it may result in rough running or premature breakdown.


editor by czh 2023-01-13
China DIN6 DIN7 Standard Gear Racks Mod2 2.5 3 4 5 corrections gear rack
Item Description
DIN6 DIN7 Standard Gear Racks Mod2 2.5 3 4 5
Helical tooth rackdrive is a lot more efficient and smoother than straight enamel rack.
In contrast with the ball screw generate, the rack and pinion drive has lower cost and is not straightforward to bend underneath extended-distance and heavy load. Compared with belt transmission, it has massive transmission electrical power, prolonged support lifestyle, steady operation and high dependability. It can ensure a continual transmission ratio and can transmit movement amongst 2 axis at any angle. It is commonly utilised in modern day mechanical transmission
.
2. Product Parameter (Specification)
three. Product Function And Software
(1) Material: 40Cr Steel, S45C Metal/C45 Steel/1045 Gentle Metal (Black Shade, White Color)
(two) Teeth: Helical/Bevel Teeth (Spur/ Straight Tooth can be chosen)
(3)Module: M1, M1.25, M1.5, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M8, M10
(4)Therapy: Grinding, Complete-milling
four.Product Details
one.Zero backlash/high precision
2.Substantial payload
three.Lower noise offered
four.Supplies and colours can be decided on
5.Effortless to be butt into any size
six.Numerous choices for surface treatment
Firm Information
|
US $4.8 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Optional |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 6.6/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
|
US $4.8 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Optional |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 6.6/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
How to Compare Different Types of Spur Gears
When comparing different types of spur gears, there are several important considerations to take into account. The main considerations include the following: Common applications, Pitch diameter, and Addendum circle. Here we will look at each of these factors in more detail. This article will help you understand what each type of spur gear can do for you. Whether you’re looking to power an electric motor or a construction machine, the right gear for the job will make the job easier and save you money in the long run.
Common applications
Among its many applications, a spur gear is widely used in airplanes, trains, and bicycles. It is also used in ball mills and crushers. Its high speed-low torque capabilities make it ideal for a variety of applications, including industrial machines. The following are some of the common uses for spur gears. Listed below are some of the most common types. While spur gears are generally quiet, they do have their limitations.
A spur gear transmission can be external or auxiliary. These units are supported by front and rear casings. They transmit drive to the accessory units, which in turn move the machine. The drive speed is typically between 5000 and 6000 rpm or 20,000 rpm for centrifugal breathers. For this reason, spur gears are typically used in large machinery. To learn more about spur gears, watch the following video.
The pitch diameter and diametral pitch of spur gears are important parameters. A diametral pitch, or ratio of teeth to pitch diameter, is important in determining the center distance between two spur gears. The center distance between two spur gears is calculated by adding the radius of each pitch circle. The addendum, or tooth profile, is the height by which a tooth projects above the pitch circle. Besides pitch, the center distance between two spur gears is measured in terms of the distance between their centers.
Another important feature of a spur gear is its low speed capability. It can produce great power even at low speeds. However, if noise control is not a priority, a helical gear is preferable. Helical gears, on the other hand, have teeth arranged in the opposite direction of the axis, making them quieter. However, when considering the noise level, a helical gear will work better in low-speed situations.
Construction
The construction of spur gear begins with the cutting of the gear blank. The gear blank is made of a pie-shaped billet and can vary in size, shape, and weight. The cutting process requires the use of dies to create the correct gear geometry. The gear blank is then fed slowly into the screw machine until it has the desired shape and size. A steel gear blank, called a spur gear billet, is used in the manufacturing process.
A spur gear consists of two parts: a centre bore and a pilot hole. The addendum is the circle that runs along the outermost points of a spur gear’s teeth. The root diameter is the diameter at the base of the tooth space. The plane tangent to the pitch surface is called the pressure angle. The total diameter of a spur gear is equal to the addendum plus the dedendum.
The pitch circle is a circle formed by a series of teeth and a diametrical division of each tooth. The pitch circle defines the distance between two meshed gears. The center distance is the distance between the gears. The pitch circle diameter is a crucial factor in determining center distances between two mating spur gears. The center distance is calculated by adding the radius of each gear’s pitch circle. The dedendum is the height of a tooth above the pitch circle.
Other considerations in the design process include the material used for construction, surface treatments, and number of teeth. In some cases, a standard off-the-shelf gear is the most appropriate choice. It will meet your application needs and be a cheaper alternative. The gear will not last for long if it is not lubricated properly. There are a number of different ways to lubricate a spur gear, including hydrodynamic journal bearings and self-contained gears.
Addendum circle
The pitch diameter and addendum circle are two important dimensions of a spur gear. These diameters are the overall diameter of the gear and the pitch circle is the circle centered around the root of the gear’s tooth spaces. The addendum factor is a function of the pitch circle and the addendum value, which is the radial distance between the top of the gear tooth and the pitch circle of the mating gear.
The pitch surface is the right-hand side of the pitch circle, while the root circle defines the space between the two gear tooth sides. The dedendum is the distance between the top of the gear tooth and the pitch circle, and the pitch diameter and addendum circle are the two radial distances between these two circles. The difference between the pitch surface and the addendum circle is known as the clearance.
The number of teeth in the spur gear must not be less than 16 when the pressure angle is twenty degrees. However, a gear with 16 teeth can still be used if its strength and contact ratio are within design limits. In addition, undercutting can be prevented by profile shifting and addendum modification. However, it is also possible to reduce the addendum length through the use of a positive correction. However, it is important to note that undercutting can happen in spur gears with a negative addendum circle.
Another important aspect of a spur gear is its meshing. Because of this, a standard spur gear will have a meshing reference circle called a Pitch Circle. The center distance, on the other hand, is the distance between the center shafts of the two gears. It is important to understand the basic terminology involved with the gear system before beginning a calculation. Despite this, it is essential to remember that it is possible to make a spur gear mesh using the same reference circle.
Pitch diameter
To determine the pitch diameter of a spur gear, the type of drive, the type of driver, and the type of driven machine should be specified. The proposed diametral pitch value is also defined. The smaller the pitch diameter, the less contact stress on the pinion and the longer the service life. Spur gears are made using simpler processes than other types of gears. The pitch diameter of a spur gear is important because it determines its pressure angle, the working depth, and the whole depth.
The ratio of the pitch diameter and the number of teeth is called the DIAMETRAL PITCH. The teeth are measured in the axial plane. The FILLET RADIUS is the curve that forms at the base of the gear tooth. The FULL DEPTH TEETH are the ones with the working depth equal to 2.000 divided by the normal diametral pitch. The hub diameter is the outside diameter of the hub. The hub projection is the distance the hub extends beyond the gear face.
A metric spur gear is typically specified with a Diametral Pitch. This is the number of teeth per inch of the pitch circle diameter. It is generally measured in inverse inches. The normal plane intersects the tooth surface at the point where the pitch is specified. In a helical gear, this line is perpendicular to the pitch cylinder. In addition, the pitch cylinder is normally normal to the helix on the outside.
The pitch diameter of a spur gear is typically specified in millimeters or inches. A keyway is a machined groove on the shaft that fits the key into the shaft’s keyway. In the normal plane, the pitch is specified in inches. Involute pitch, or diametral pitch, is the ratio of teeth per inch of diameter. While this may seem complicated, it’s an important measurement to understand the pitch of a spur gear.
Material
The main advantage of a spur gear is its ability to reduce the bending stress at the tooth no matter the load. A typical spur gear has a face width of 20 mm and will fail when subjected to 3000 N. This is far more than the yield strength of the material. Here is a look at the material properties of a spur gear. Its strength depends on its material properties. To find out what spur gear material best suits your machine, follow the following steps.
The most common material used for spur gears is steel. There are different kinds of steel, including ductile iron and stainless steel. S45C steel is the most common steel and has a 0.45% carbon content. This type of steel is easily obtainable and is used for the production of helical, spur, and worm gears. Its corrosion resistance makes it a popular material for spur gears. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of steel.
A spur gear is made of metal, plastic, or a combination of these materials. The main advantage of metal spur gears is their strength to weight ratio. It is about one third lighter than steel and resists corrosion. While aluminum is more expensive than steel and stainless steel, it is also easier to machine. Its design makes it easy to customize for the application. Its versatility allows it to be used in virtually every application. So, if you have a specific need, you can easily find a spur gear that fits your needs.
The design of a spur gear greatly influences its performance. Therefore, it is vital to choose the right material and measure the exact dimensions. Apart from being important for performance, dimensional measurements are also important for quality and reliability. Hence, it is essential for professionals in the industry to be familiar with the terms used to describe the materials and parts of a gear. In addition to these, it is essential to have a good understanding of the material and the dimensional measurements of a gear to ensure that production and purchase orders are accurate.


editor by czh 2022-12-14